Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
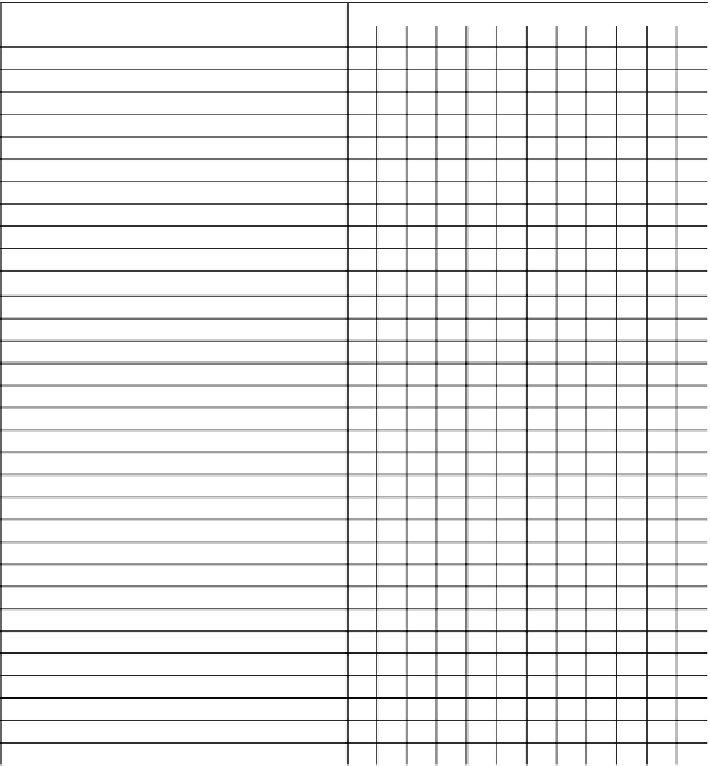
Table 6
Timing of chlorpyrifos use for crops in the U.S. that are in the field part of the year
Months of the year in which CPY is applied
JFMAMJ JASOND
Crop in field, location, and use of CPY
Corn,
Southern states in field
Use of CPY
Northern states in field
Use of CPY
Cotton,
Southern areas in field
Use of CPY
Northern areas + CA in field
Use of CPY
Peanuts
, in field
Use of CPY
Peppermint and Spearmint
, in field
Use of CPY
Sorghum
, in field
Use of CPY
Soybeans
, in field
Use of CPY
Sugarbeets
, in field Imperial Valley, CA
Use of CPY
Other locations in field
Use of CPY
Sunflowers
, in field CA
Use of CPY
TX & OK in field
Use of CPY
Other states in field
Use of CPY
Sweet potato,
in field
Use of CPY
Tobacco,
in field New England & PA
Use of CPY
Southern states in field
Use of CPY
Data from: (Chen et al. 2011; USDA 2010; Zheljazkov et al. 2010)
Half-lives for hydrolysis in water are inversely dependent on pH, and range from
16 to 73 d. CPY is an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and is potentially toxic to
most animals. Differences in susceptibility result from differences in rates of adsorp-
tion, distribution, metabolism, and excretion among species. CPY is an important
tool in management of a large number of pests (mainly insects and mites) and is
used on a wide range of crops in the U.S. Estimates of annual use in the U.S. from
2008 to 2012 range from 3.2 to 4.1 M kg y
−1
, which is about 50% less than the
amount used prior to 2000. Applications to corn and soybeans accounts for 46-50%
of CYP's annual use in the U.S.











































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search