Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
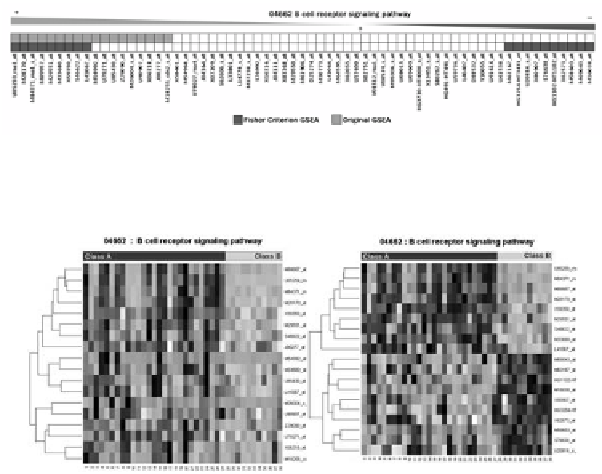
Fig. 10.
Comparison of statistically significant genes identified by original-GSEA and FC-GSEA
(bright grey boxes: results by original-GSEA, dark grey boxes: results by FC-GSEA)
(a) Original-GSEA (b) FC-GSEA
Fig. 11.
Heat maps of statistically significant genes identified by (a) original-GSEA and (b)
FC-GSEA
As can be seen in Fig. 10, original GSEA that employs SNR-based gene ranking
has the characteristics that the significant genes are selected by taking either genes
whose SNR values are large in a positive region or genes whose SNR values are large
in a negative region from the reference point. Consequently, the resulting significant
genes are shown to have either only the highly up-regulated genes, as in Fig. 11 (a), or
only the highly down-regulated genes in one group over the other. On the other hand,
FC-GSEA that employs FC-based gene ranking has the characteristics that significant
genes are chosen in such a way to take genes whose FC values are large in a positive
region, i.e. genes having the relatively large expression difference between two
groups. Thus, the resulting significant genes are shown, as in Fig. 11 (b), to have
highly up-regulated genes and highly down-regulated genes together.
4.2 Finding Leukemia-Related Pathways
Specifically, from
literatures
[15, 16, 17], we first identified five pathways which are
known to show the difference between AML and ALL types, i.e.
hsa04110
(cell cy-
cle),
hsa04210
(apoptosis),
hsa04660
(T cell receptor signaling pathway),
hsa04662
(B cell receptor signaling pathway), and
hsa04640
(hematopoietic cell lineage). Two
pathways including
hsa00480
(Glutathione metabolism) and
hsa00980
(Metabolism
of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450) were obtained by taking the ones having p-value
≤0.05 by
Fisher's exact test
[19], out of the KEGG pathways including the AML-
related or ALL-related genes identified from the Genetic Association Database
Search WWH ::

Custom Search