Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
In the second case,
r
is equal to
IRR
at 0,17. In this case, the UBMSS also finds
the investment acceptable.
The third case is where r > IRR and both indicators take negative values. This
case represents an unacceptable investment.
The results presented show the decision taken by the UBMSS after analysing
not only the rates, but also the relationship between them. This kind of analysis
can be undertaken if the significance of a change in one rate on the change in the
second rate is determined.
Another example of a UBMSS system is presented in chapter 4.4 below, which
discusses such a system analysing three selected economic and financial ratios.
4.4 An Exa mple UBMSS System for a M ulti-factor Anal ysis
4.4 An Example UBMSS System for a Multi-factor Analysis
of the Economic and Financial Ratios
4.4 An Exa mple UBMSS System for a M ulti-factor Anal ysis
This chapter presents a UBMSS system interpreting three selected economic indi-
cators, namely:
•
NPV - net present value (symbol: W1);
•
r
- discount rate (symbol: W2);
•
IRR - internal rate of return (symbol: W3).
For the proposed UBMSS system, the following formal grammar has been
defined:
G
=
(
Σ
,
Σ
P
,
S
)
w
N
T
,
w
w
w
w
where:
Σ
- denotes the set of non-terminal symbols defined as follows:
N
w
Σ
={RESULTS,
W1,
W2,
W3,
WEAK_ACCEPT,
ACCEPT,
N
w
STRONG_ACCEPT, NOT_ACCEPT, A, B, C, D, E},
Σ
- denotes the set of terminal symbols defined as follows:
T
w
Σ
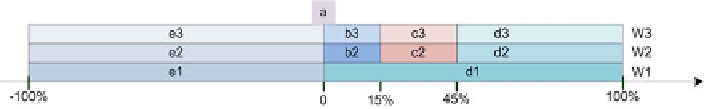
′a′, ′b′, ′c′, ′d′, ′e′}, and the individual elements of this set take the fol-
lowing values: a = {0%}, b
ϵ
(0%, 15%], c
ϵ
(15%, 45%), d
ϵ
[45%, 100%], e
ϵ
[-
100%, 0%) (Fig. 4.7).
={
T
w
Fig. 4.7.
Terminal symbols for the
G
w
grammar