Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
based on the expert information possessed (for example in the form of knowledge
bases) and the processes of machine (computer) perception and understanding of
data performed with the use of e.g. mathematical linguistics.
In cognitive categorisation systems, the interpreted data, due to its semantics,
will also be described, analysed and used for reasoning, which may mean that the
analysed data will not only be correctly processed, but also learned and under-
stood. The detailed description of the data analysis process taking place in cogni-
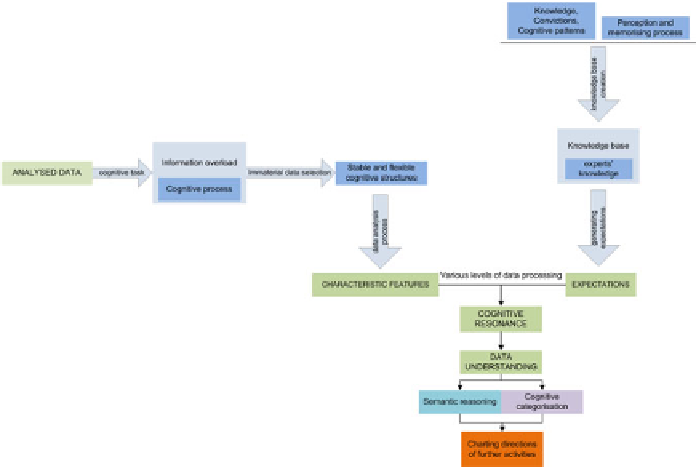
tive categorisation systems is presented in Figure 3.2.
Fig. 3.2.
The data analysis process in cognitive categorisation systems
Cognitive categorisation systems analyse data following human cognitive proc-
esses in which various information processing stages can be distinguished. In the
case of cognitive categorisation systems, information is not the only type of data
that can be subjected to cognitive categorisation processes which borrow the
methods of executing processes composed of various operations from classical in-
formation processing. Thanks to these processes, the course of the stimuli received
by the system (outside data) is optimised during the executed process. This proc-
ess is equated to the assumption of the economical course of processes taking
place (necessary in the analysis). This is why significant cognitive tasks (for the
analysis process) are determined for the data undergoing analyses, which leads to
the correct description of the cognitive process. During the description of the cor-
rect cognitive process, an information overload can take place. This overload can
be eliminated only if a stage of selecting data that is immaterial (form the point of
view of the analysis conducted) is introduced. This selection, which is possible
because the system has a king of 'attention' directed at eliminating superfluous