Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
recognition process and the threats posed by a whole range of system interference.
In this case it consisted in the noise, din and the distance between the students,
whereas in the system analysis there is no distance difference, but undoubtedly
various other sources of interference can appear.
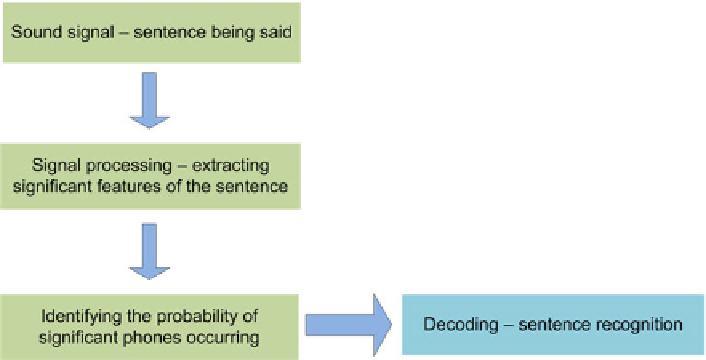
A diagram of the process of recognising speech as a sound signal is presented
in Fig. 2.19.
Fig. 2.19.
Stages in the speech recognition process
This diagram shows the speech recognition process from the moment the sen-
tence is pronounced and becomes a sound signal for the system until the moment
the sentence is recognised. The input sound signal undergoes signal processing to
extract significant features (usually acoustic) of the sentence, and then the prob-
ability of the occurrence of individual phones of major significance for the ana-
lysed sentence is identified. This probability can be determined using probability
calculus methods or neural networks. After the probability of occurrence of sig-
nificant phones has been determined, there comes the stage of information decod-
ing leading to recognising the sentence. This way, the entire speech recognition
process is executed.
Another type of recognition analysis is recognising the speaker, i.e. the person
pronouncing the given words. In this analysis it is not the content of the statement
that is analysed, but only the person making that statement, so the speech signal is
analysed to enable distinguishing different speakers from one another not only if
they say different statements, but primarily when their statements are similar or
identical. This is why the entire speaker recognition process starts by creating the
appropriate base of expected speakers from which the analysing system will select
the ideal speaker, i.e. the one who ideally corresponds to the system, or will an-
nounce the lack of one due to no or too little consistency between the speaker and
the speaker patterns kept in the system. If the system has a properly designed da-
tabase containing a certain (large) number of reference models for which the