Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
must the dissolution procedure be developed and validated, but also any analytical
technique used for the assay.
7.4.1
Q
uAlIfIcAtIon
And
c
AlIbrAtIon
Prior to undertaking the task of dissolution procedure development and validation, it is
necessary to invest some time and energy up-front to ensure that the dissolution system
itself is validated, or
qualified.
. Qualification is a subset of the overall validation process
that verifies proper module and system performance prior to the instrument being
placed on-line in a regulated environment, and additional information about Analytical
Instrument Qualification (AIQ) can be found in Chapter 2 of this volume. Analysts for
years have used prednisone and salicylic acid tablets to qualify and “chemically” cali-
brate dissolution instruments. Figure 7.8 illustrates example HPLC methods commonly
0.06
0.0
3.0
Time in Minutes
(a)
0.022
0.0
6.0
Time in Minutes
(b)
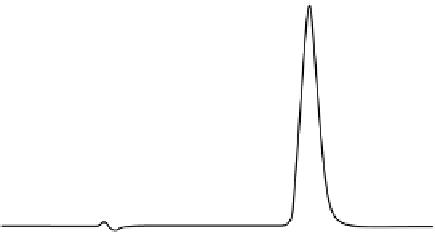
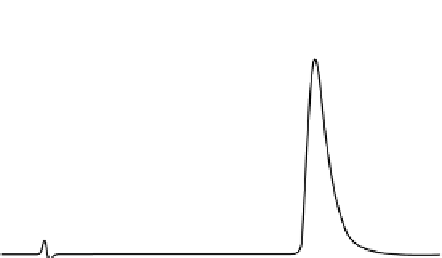
FIgure 7.8
Example chromatograms from methods used for the chemical calibration or
qualification of a dissolution system by HPLC. (a) HPLC separation of a 20-µL injection of a
0.01 mg/mL (in water) prednisone USP standard. Column: 3.9 by 50 mm C
18
. A mobile phase of
water/methanol 50/50, at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min was used. Detection was by UV at 254 nm.
(b) HPLC separation of a 20-µL injection of a 0.1 mg/mL (in water) salicylic acid USP standard.
Column: 3.9 by 50 mm C
18
. A mobile phase of 1.6% acetic acid/methanol 85/15, at a flow rate
of 1.0 mL/min was used. Detection was by UV at 270 nm.