Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
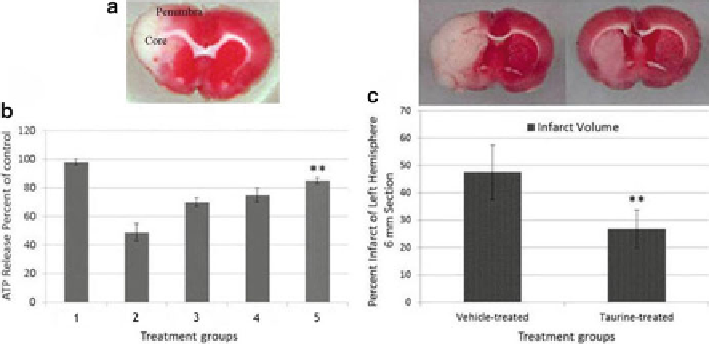
Fig. 23.1
Effect of Taurine on cell viability in primary neuronal cell culture and TTC on MCAO
model of stroke. (
a
) Core and penumbra of the lesion part of the left hemisphere. (
b
) Dose-
dependent neuroprotection of taurine against hypoxia/reoxygenation. (1) Control; (2) hypoxia; (3)
hypoxia + 1 mM taurine; (4) hypoxia + 5 mM taurine; (5) hypoxia + 10 mM taurine. Cell viability
was measured by ATP assay. Control values were fixed at 100%. The values for Hyp and Tau + Hyp
were normalized relative to the control values and represent mean±SEM of five preparations
(**
p
< 0.01 versus hypoxia). (
c
) Effects of taurine on infarct volume of 6 mm section on day 4 of
reperfusion after 2 h of focal cerebral ischemia. Vehicle or taurine was injected subcutaneously
24 h after ischemia. The infarct zone was displayed by TTC staining in treated rats. Sham-operated
group showed no infarct zone. Representative images are slices of 6 mm section from the frontal
pole. Data were presented as mean ± SD,
n
= 16 (**
p
< 0.05 vs. vehicle)
threefold over control cultures. After treatment with taurine, followed by hypoxia/
reoxygenation, however, the levels of ATF4 in cortical neurons is similar to that of
hypoxia/reoxygenation alone (Fig.
23.2a
), indicating that taurine does not inhibit
the initiation of the PERK pathway under this condition. Similarly, the expression
of ATF4 in the MCAO model does not change with taurine treatment in the core of
the infarct by comparison with the vehicle-treated group (Fig.
23.2b
). These results
indicate that taurine has no observable effects on PERK pathway activation in either
cortical neurons or in the MCAO stroke model.
We next examined the effect of taurine on the ATF6 pathway in cortical neurons
subjected to hypoxia/reoxygenation and in the brain of rats subjected to MCAO
occlusion. After dissociation from GRP78, ATF6 translocates from the ER to the
Golgi apparatus where it is cleaved to its active form (Chen et al.
2002
) . Treatment
with taurine considerably reduced the level of cleaved ATF6 in both primary neu-
ronal cultures and in the core of the infarct of MCAO rats. Interestingly, the ratio of
cleaved ATF6 to ATF6 in neurons and MCAO rats treated with taurine dramatically
declined by approximately 50% relative to neurons under hypoxia/reoxygenation or
MCAO rats, respectively, in the absence of taurine as shown in Fig.
23.3a, b
. These
results demonstrate that taurine can prevent the activation of the ATF6 pathway
in vitro and in vivo. To determine if taurine can affect the IRE1 pathway, we tested
the expression of p-IRE1 in rat primary cortical neurons under hypoxia/reoxygenation
Search WWH ::

Custom Search