Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
8
8
Liver
Plasma
7
7
6
6
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
0
0
Control
NAC
TAU
TTAU
APAP
NAC +
APAP
TAU +
APAP
TTAU +
APAP
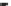
Fig. 20.9
The effects of NAC, TAU, and TTAU on the liver and plasma activities of GCS of rats
treated with a hepatotoxic (800 mg/kg i.p.) dose of APAP. Differences were significant from control
at *
p
< 0.05 and from APAP at
†
p
<0.05 and
††
p
<0.01. Values are shown as mean ± SEM for
n
= 6
NAPQI through conjugation with GSH (Spielberg
1985
). Relative to control val-
ues, APAP drastically lowered the plasma and hepatic activity of g-GCS by 61%
and 70% (
p
< 0.001), respectively (Fig.
20.9
). A pretreatment with TTAU virtually
reversed the effects (£3% decrease) and one with TAU was markedly protective
(−19%,
p
< 0.05, and −8%, respectively). NAC was equipotent with TTAU.
GSTs are a group of cytosolic and membrane-associated isoenzymes with the
ability to catalyze the nucleophilic addition of the thiol of reduced glutathione
to a variety of electrophiles (Hayes and Strange
1995
; Rushmore and Pickett
1993
). At low doses of APAP, GST is responsible for the bulk of the detoxification
of NAPQI through conjugation with GSH (Henderson et al.
2000
; Ketterer et al.
1983
). However, a protective role for GST in APAP overdoses has been ques-
tioned after experiments showing that mice nulled for GST became resistant to
the hepatotoxicity of APAP and that wild and nulled animals showed no differ-
ence in APAP metabolism and the same degree of APAP-reactive metabolites
binding to cellular proteins, thus indicating that GST does not contribute in vivo
to the formation of GSH conjugates of APAP but instead plays an unexpected
role in the toxicity of this compound (Henderson et al.
2000
) .
Under the present experimental conditions, the plasma activity of GST was
found to be reduced by APAP significantly (
p
< 0.001) in the plasma (by 70%)
and liver (by 61%) when compared to control values (Fig.
20.10
). These
decreases were more than halved in the plasma (28-31% decreases,
p
< 0.01)
and nearly halved (34-42% decreases,
p
< 0.01) in the liver by a pretreatment








































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search