Database Reference
In-Depth Information
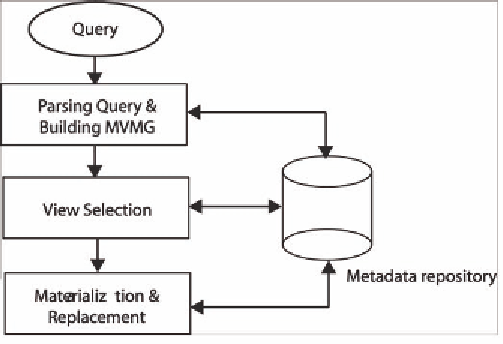
Figure 4. MATUN architectual overview
Overview of our Tool
based on the time it takes to answer a query and
the algorithm used to estimate the number of disk
pages needed to store the result set. However,
these statistics are often misleading because of
caching mechanisms used by the data source and
optimistic space estimations.
MATUN tool represents the MVMG as a
matrix, shown in Figure 5. A column represents a
single view, and a row represents a single query. A
zero simply means the view for that column is not
being used by the query; one means otherwise. The
matrix allows the expert user to evaluate frequently
used views easily.And it helps decide which views
to materialize /dematerialize manually.
Materialize Query.
The materialize query
function allows the expert-user to manually add
queries to the MVMG either from a file or by
using the build-in editor. Before a query is added
to the MVMG it is parsed into its own AND-OR
DAG. Once the query is added to the MVMG,
the BestViews algorithm decides whether or not
to materialize to query.
Dematerialize Query
. This function allows
the expert-user to clean the MVMG by deleting
a set of selected queries and all its derived views
which are not shared by other queries.
Refresh MVMG.
Using the refresh MVMG
function the expert-user can manually update
MATUN provides the expert-user with a graphical
user interface to manually add and remove queries
to and from the MVMG. Using the materialize /
dematerialize functions, the expert-user can decide
whether or not the query should be considered for
materialization / dematerialization. The material-
ize function starts the materialization process after
integrating the new query into the MVMG. Once
the expert-user decides to materialize the query,
the view selection method will decide which views
to materialize for improving the overall response
time according to their frequency, goodness and
the available storage space.
MATUN has several functions to manipulate
the MVMG manually. However, it has three pri-
mary functions which we will outline. All these
functions are available to the expert-user through
the user interface shown in Figure 6. Queries in the
MVMM can be selected to manually manipulate
their frequency, meantime and size or to simply
edit the query itself. These query statistics are used
to calculate the cost and goodness of each query.
The decision to materialize a query (or a fragment
of it) is entirely based upon these values.
MATUN provides the option to generate query
statistics automatically from a given data source
Search WWH ::

Custom Search