Database Reference
In-Depth Information
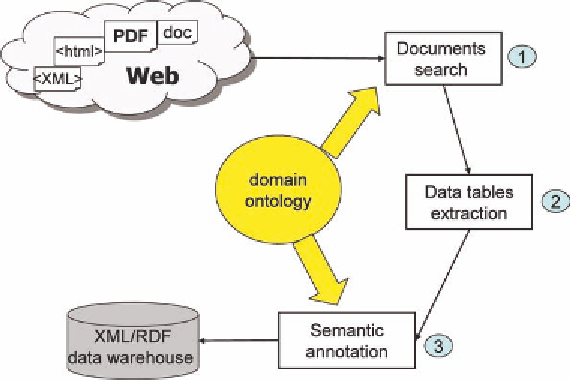
Figure 4. @WEB architecture
of our approach. But, in a lot of application
domains, especially in the scientific field, data
tables are often a source of relevant, reliable
and synthetic data. Moreover, their tabular
structure is obviously easier to automatically
parse than natural language. In the second step,
the Web documents in html or most usually in
pdf are translated into a generic XML format,
which allows the representation of data tables
in a classical and generic way -- a table is a set
of lines, each line being a set of cells. In the
third step, the tables are semantically annotated
according to the domain ontology.
The semantic annotation process of a table ex-
tracted from the web consists in identifying which
semantic relations from the domain ontology are
represented in the table. The different steps of
our semantic annotation process are detailed in
Hignette & al. (2007).
The semantic annotation process generates
RDF descriptions which represent the semantic
relations of the ontology recognized in each row
of the Web data table. Some of these RDF descrip-
tions include values expressed as fuzzy sets. The
fuzzy values used to annotate Web data tables
may express similarity or imprecision. A fuzzy
set having a semantic of similarity is associated
with each cell belonging to a symbolic column.
It represents the ordered list of the most similar
values of the ontology associated with the value
present in the cell.A fuzzy set having a semantic of
imprecision may be associated with cells belong-
ing to numerical columns. It represents an ordered
disjunction of exclusive possible values.
Example 3
Table 1 presents an example of a Web data table in
which the semantic relation
ContaminationRange
Table 1. A Web data table
Food
Contaminant
Contaminant Level (ng/g)
Basmati rice
OTA
1.65-1.95
Chili powder
OTA
2.34-4.91
Grape raisins
OTA
0.93-1.20






















Search WWH ::

Custom Search