Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
t
= l
1
+
z
1
q
2
>
0, q
1
<
0
mtls
t
= −∞
t
= ∞
t
=
0
solution locus
mdls
z
2
ols
tls
t
= l
2
−
dls
t
= l
2
+
stls
saddle locus
sdls
= l
1
−
t
z
1
q
1
, q
2
<
0
t
= l
1
+
mtls
t
= −∞
t
= ∞
t
=
0
saddle locus
mdls
z
2
ols
= l
2
−
dls
tls
t
t
= l
2
+
stls
saddle locus
sdls
t
= l
1
−
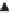
Figure 5.8
Two-dimensional case: hyperbolas and critical
loci for
q
1
<
0,
q
2
>
0and
q
1
<
0,
q
2
<
0.
locus can be determined, and this gives the best choice for the initial conditions
for the GeTLS neuron. A direct consequence is knowledge of the exact position of
the convergence barrier.
The origin of the
x
space, which coincides with the origin of the
z
space, has
some very important features as a consequence of the existence of the hyperbolas:
1. In every parametric hyperbola, the origin corresponds to the point for
t
=
−∞
; recalling that there are no zeros between this point and the GeTLS


































Search WWH ::

Custom Search