Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
first screening method developed by Stolker [97] was
subsequently published by Ortelli et al. [57]. This work describes the use of UHPLC
A similar application of the
-
TOF
MS for the screening of 150 VDs and metabolites in raw milk, estimating a
routine application of
-
50 samples per day. According to the high sensitivity and
>
selectivity of TOF
g/l, and they
were far below the correspondingMRL for the majority of the compounds (Table 6.1).
Apart from some problems with avermectins, the method allowed suitable screening
and quanti
-
MS, the limits of detection ranged from 0.5 to 25
μ
cation for the rest of VDs.
These reports demonstrated the suitability of LC
-
TOF
-
MS for the screening and
quanti
cation of VD residues in different food matrices. However, in terms of
unequivocal con
rmation, the main drawback relies on the fact that only MS data
of the protonated molecules are used in these reports. Even with very low mass error
(e.g.,
cient. In this way,
Turnipseed et al. [100] took advantage of the ability of QqTOF
10 ppm) the con
rmation of VD identities can be insuf
<
-
MS to carry out
screening and unambiguous con
rmation of 25 VDs in milk samples with precursor
ion selection. Screening of residues was accomplished by collecting TOF data, while
MS/MS data generated for the [M
H]
+
ions (SRM mode) were employed to con
rm
the presence of VD residues in the samples by monitoring product ions. Nevertheless,
screening and con
+
rmation were carried out using different methods and, in conse-
quence, nonnegative samples were reinjected for con
rmation. Although the method
was intended to be qualitative, an evaluation of the MS data indicated a linear
response and acceptable recoveries for the majority of target compounds. Moreover,
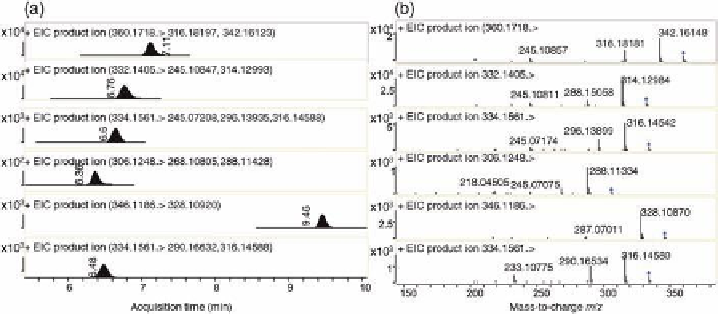
several metabolites were identi
ed evaluating MS and MS/MS data (Figure 6.3). For
example, several plausible metabolites of enro
oxacin, some of them not previously
observed in milk, were found in the samples such as cipro
oxacin (another
uo-
roquinolone that differs from enro
oxacin by an ethyl group) or des-enro
oxacin (
m
/
z
Figure 6.3.
(a) Extracted MS/MS ion chromatograms for compounds in an incurred enro
oxacin milk
sample. From the top, traces for enro
oxacin, cipro
oxacin, and the proposed metabolites desethylene
enro
oxacin, descipro
oxacin, and oxocipro
oxacin are shown. For comparison, the bottom MS/MS
chromatogram is for a standard of pe
oxacin. (b) Product ion spectra for these compounds.
Source
:
Ref. [100], Figure 4, p. 7577. Reproduced with permission of American Chemical Society.