Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Well Monitoring
Water
Level
Spill Observation Well
1
Storage I/O Well
Water Well
Gathering System
3
Shallow Water Supply
2
Boundary
Storage
Project
Upper Caprock
5
Gas Reservoir
Possible
Spill Area
Water Bearing Zone
4
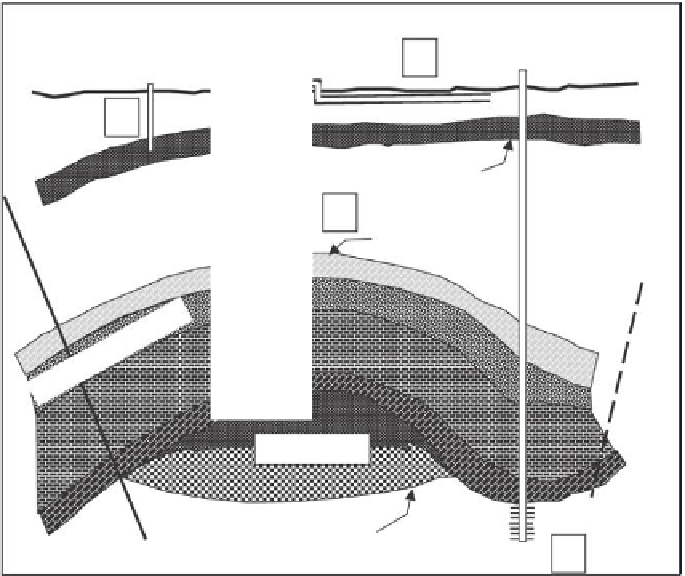
FIGURE 8.3
Gas storage system areas for natural gas monitoring. 1. Ground surface. 2. Wellbores. 3. Shallow
water wells. 4. Reservoir spill point. 5. Permeable zone above caprock. (Modified from Katz, D.
L., and K. H. Coats. 1968.
Underground Storage of Fluids
, Ulrich's Books.)
Depleted Reservoir Storage
The most common type of underground gas storage occurs in shallow, high
deliverability depleted oil and gas reservoirs. Although the requirements
vary, typically these reservoirs require 50% base gas (i.e., equal amounts of
base and working gases) and present several advantages:
• They are near existing regional pipeline infrastructures.
• They have a number of usable wells and field gathering facilities to
reduce the cost of conversion to gas storage.
• Their geology is well known; they contain previously trapped hydro-
carbons that minimize the risks of reservoir “leaks.”
Some disadvantages are associated with depleted reservoirs. Because of
the nature of the reservoir-producing mechanisms, working gas volumes
are usually cycled only once per season (extremely high deliverability stor-
age reservoirs are exceptions). Often, these reservoirs are old and require