Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
2.3
2.2
Charge voltage
Open circuit voltage (OCV)
2.1
2.0
Discharge voltage
1.9
1.8
1.7
0
100
200
300
Depth of Discharge/Ah
400
500
600
700
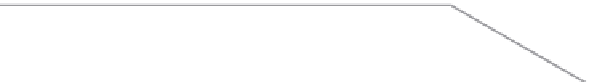
FIGURE 6.2
NaS cell voltage characteristics. (Courtesy of NGK Insulators Ltd.)
(temperature or depth of discharge). If the discharge continues past Na
2
S
3
,
another two-phase mixture again forms, but now the second phase is solid
Na
2
S
2
. The formation of Na
2
S
2
in a cell is undesirable because high internal
resistance, very poor rechargeability, and structural damage to the electro-
lyte can result.
Several other important characteristics of the sodium-sulfur electro-
chemical couple are evident from Figure 6.2. At high states of charge, the
working voltage during charge increases dramatically due to the insu-
lating nature of pure sulfur (shown also by the higher cell resistance).
This same factor also causes a slight decrease in cell voltage at the start
of discharge. At the C/3 discharge rate, the average cell working volt-
age is approximately 1.9 V. The theoretical specific energy of the electro-
chemical couple is 755 Wh/kg (to 1.76 V open circuit). Although not all
of the sodium is recovered during the initial charge, cells subsequently
deliver 85 to 90% of their theoretical ampere-hour capacity. Finally, the
existence of wholly molten reactants and products eliminates the classical
morphology-based electrode aging mechanisms, thus yielding an intrinsi-
cally high cycle life.
Compared to vanadium redox batteries (VRBs), NaS batteries have the
advantage of extremely quick response time, making them more suitable
for power quality applications (smoothing short term spikes in demand).
It is believed that these advantages along with better round-trip efficiency
are the reasons NaS batteries currently seem to have an edge with utilities
seeking to delay transmission and distribution upgrades. American Electric
Power (AEP) recently installed a $2.5 million, 7.2 MWh battery as described
in Case Study 1.