Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
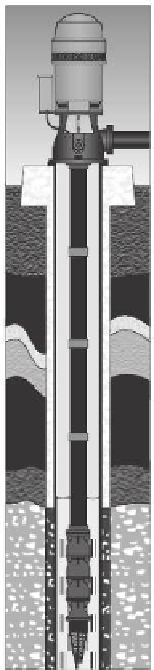
FIGURE 4.7
Example of submersible vertical turbine pump. (Figure courtesy of American Turbine Vertical
Turbine and Submersible Pumps. http://americanturbine.net/sites/americanturbine.net/files/
brochures/vertical-turbine-submersible-pump-brochure.pdf)
be capable of operating in reverse as a turbine at efficiencies in the range
of 65 to perhaps 85%.
10
This method is proposed as a preferred option for
the aquifer UPHES situation because it uses existing technology, is commer-
cially available, and represents a low cost solution. Because of the difficulty
in predicting turbine performance of a specific centrifugal pump, testing is
required to characterize the flow capability, water velocity range, and tur-
bine efficiency. The selected centrifugal pump design must employ a keyed
shaft to accommodate shaft torque in either direction.
Centrifugal motor pumps are commonly used for pumping water in many
situations. They are available in submerged or nonsubmerged designs, with
a wide range of available head ratings, flow ratings, and power ratings for
commercial versions. These units are commonly centrifugal or vertical tur-
bine designs, integrated with AC induction motors. The industry standard