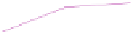Database Reference
In-Depth Information
70
1 slave
2 slaves
3 slaves
4 slaves
60
5 slaves
6 slaves
7 slaves
8 slaves
9 slaves
10 slaves
50
11 slaves
40
30
20
10
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
Number of concurrent users
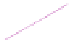
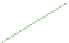
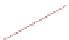
Fig. 6.7
End-to-end throughput with 80/20 read/write ratio and 600 initial data size in different
regions
is in the saturation status, adding more slaves does not help with improving the
scalability because the overloaded master fails to offer extra capacity for improving
write throughput to maintain the read/write ratio that corresponds to the increment
of the read throughput. Hence, the read throughput is constrained by the benchmark,
for the purpose of maintaining the predefined read/write ratio at 50/50. The slaves
are over provisioned in the case of 3 and 4 slaves, as the suppressed read throughput
prevents slaves from being fully utilized. The similar saturation transition also
happens to 3 slaves at 50/50 ratio in different zones and different regions in Figs.
6.3
and
6.4
respectively, 10 slaves at 80/20 ratio in the same zone and different zones
in Figs.
6.5
and
6.6
respectively, and also 9 slaves at 80/20 ratio in different regions
in
6.7
.
The configuration of the geographic locations is a factor that affects the end-to-
end throughput, in the context of locations of users. In the case of our experiments,
since all users emulated by Cloudstone send read operations from
us-east-1a
,
distances between the users and the slaves increase by following in the order of
same zone, different zones and different regions. Normally, a long distance incurs
a slow round-trip time, which results in a small throughput for the same workload.
Therefore, it is expected that a decrease of maximum throughput can be observed
when configurations of locations follow the order of same zone, different zones
and different regions. Moreover, the throughput degradation is also related to
read percentages, the higher percentage the larger degradation. It explains why
degradation of maximum throughput is more significant with the configuration of