Database Reference
In-Depth Information
6.3
Trade-Off Analysis of Virtualized Database Servers
End-to-End Throughput
Figure
6.2
to
6.7
show the throughput trends for up to 4 and 11 slaves with mixed
configurations of three locations and two read/write ratios. Both experiment results
indicate that MySQL with asynchronous master-slave replication is limited to scale
due to the saturation that happened to the master database.
In particular, the throughput trends react to saturation movement and transition
in virtualized database replica servers in regard to an increasing workload and
an increasing number of replica servers. In general, the observed saturation point
(the point right after the observed maximum throughput of a number of slaves),
appearing in slaves at the beginning, moves along with an increasing workload
when more slaves are synchronized to the master. But eventually, the saturation will
transit from slaves to the master where the scalability limit is achieved. Taking the
Fig.
6.5
of throughput trends with configurations of same zone and 50/50 ratio as an
example, the saturation point of 1 slave is initially observed under 100 workloads
due to the full utilization of the slave's CPU. When a 2
nd
slave is attached, the
saturation point shifts to 175 workloads where both slaves reach their maximum
CPU utilization while the master's CPU usage rate is also approaching its limit.
Thus, ever since the 3
rd
slave is added, 175 workloads remain as the saturation
point, but with the master being saturated instead of the slaves. Once the master
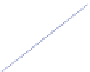
25
20
15
10
1 slave
2 slaves
3 slaves
4 slaves
5
0
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
Number of concurrent users
Fig. 6.2
End-to-end throughput with 50/50 read/write ratio and 300 initial data size in the same
zone