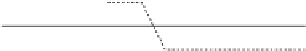Database Reference
In-Depth Information
≤ i ≤
2
β
(ii)
Find the
iβ
n-th quantiles for this set,
1
.
algorithm on A and B, for the computed
2
β
(iii)
Run the
LCSS
δ,ε
set of
translations.
(iv)
Return the highest result.
5. Indexing Trajectories for Similarity Retrieval
In this section we show how to use the hierarchical tree of a clustering
algorithm in order to eciently answer nearest neighbor queries in a dataset
of sequences.
The distance function
2 is not a metric because it does not obey
the triangle inequality. This makes the use of traditional indexing tech-
niques dicult. An example is shown in Figure 12, where we observe
that
D
) = 1, therefore the
respective distances are both zero. However, obviously
LCSS
(
δ, ε, A, B
)=1and
LCSS
(
δ, ε, B, C
D
2(
δ, ε, A, C
)
>
D
)=0+0.
We can however prove a weaker version of the triangle inequality, which
can help us avoid examining a large portion of the database objects. First
we define:
2(
δ, ε, A, B
)+
D
2(
δ, ε, B, C
LCSS
δ,ε,F
(
A, B
)=max
fc∈F
LCSS
δ,ε
(
A, f
c
(
B
))
Clearly,
−
LCSS
δ,ε,F
(A
,
B)
D
2(
δ, ε, A, B
)=1
min(
|A|, |B|
)
Fig. 12.
An example where the triangle inequality does not hold for the new
LCSS
model.