Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Ohm's Law
One of the most frequently used formulas in electronics is Ohm's law, which
states that the current that l ows through a conductor between two points
is directly proportional to the potential difference between the two points.
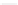
Figure 3-1 depicts Ohm's Law.
I
V
R
I =
V
R
Figure 3-1:
Ohm's Law
In this Ohm's Law formula,
I
is the l ow of current,
V
is the potential differ-
ence, and
R
is the resistance of the conductor in ohms. For example, imagine a
50 Ω resistor placed on the ends of a 1.5 V AA battery. In this case, the formula
would appear as shown in Figure 3-2.
I
V
R
I =
1.5
50
1.5V
50 Ω
I =
I = 30 mA
Figure 3-2:
Ohm's Law example
I
is unknown. However, both
V
and
R
are known, so
I
can be calculated.
V
is the voltage of the battery (1.5 volts) and
R
is the resistive value of the resis-
tor (50). Knowing these two values, you can now calculate the current l owing
inside the resistor—0.3 amps, or 30 milliamps.
The Basic Components
Looking at a circuit board, you might be afraid of all the different components
on the board, all the different types.... How can you possibly understand all
that? In truth, there are relatively few electronic components, and most are
















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search