Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
at 84 MHz and is a full 32-bit device. It has a large amount of digital and
analog I/O: 54 digital pins (12 of which can be used as PWM) and 12 analog
inputs. The board has 4 UARTs, an SPI header, a Twin-Wire Interface, and
even includes a JTAG header.
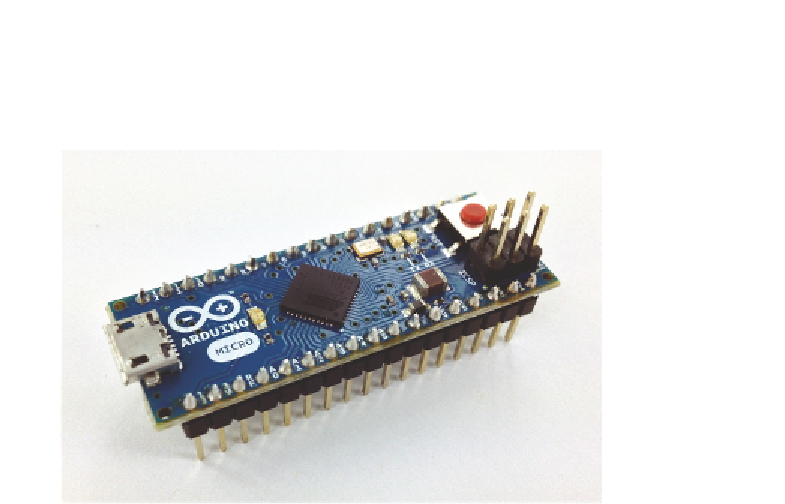
Figure 1-8:
The Arduino Micro
The Arduino Due has more strict power supply requirements, and the micro-
controller itself is powered under 3.3 V. Be careful not to apply 5 V to any of the
pins: otherwise, you will damage the board. When choosing a shield for the
Due, make sure the shield supports 3.3 V. You can identify if a shield is Due
compatible by making sure it conforms to the Arduino R3 layout.
The Arduino Due is an incredibly powerful Arduino. The Due has 512 KB of
l ash memory and a total of 96 KB of SRAM. It can handle the largest programs
at a fast speed. If you have a lot of calculations to perform, this is the Arduino
that you need (Figure 1-9).
LilyPad Arduino
The LilyPad Arduino is an interesting device. It strays from the typical Arduino
build because it is not rectangular, but round. Secondly, it does not support
shields. What it is designed for, however, is to be a small device that is perfect
for wearable computing, or e-fabric. The round shape means that connectors
are evenly distributed, and its small scale (2 inches in diameter) makes it perfect
for wearable devices. This device is easily hidden, and multiple manufacturers
have designed devices especially for the LilyPad: Wearable LEDs, light sensors,
even battery supply boxes that can be sewn into fabric.




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search