Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
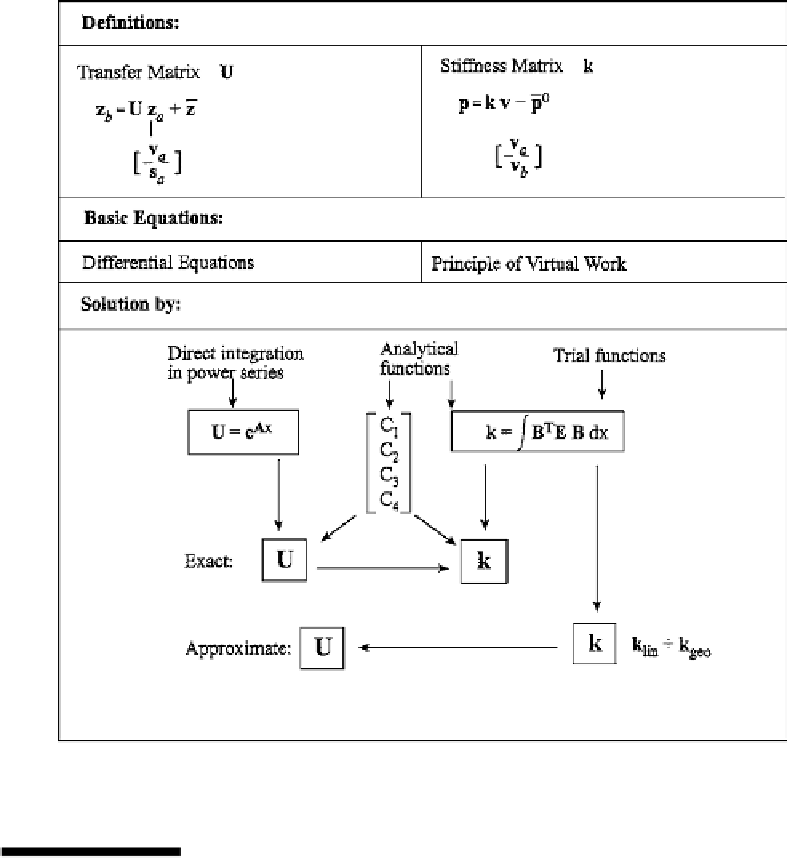
TABLE 11.4
Evaluation Methods for Element Matrices
11.4
System Analysis (Theory of Second Order)
To evaluate the stability of structural systems, the displacement method of Chapters 4, 5
and 6 can be applied, although heretofore the displacement method was utilized for linear
systems. For the system analysis, the element stiffness matrices
k
lin
(such as
k
lin
of Eq. (11.63)
for beams) are assembled to form the system stiffness matrix
K
lin
. In a similar fashion, the
geometric stiffness matrices
k
i
geo
of the elements (such as the beam
k
i
geo
of Eq. (11.64)) are
assembled into the system geometric stiffness matrix
K
geo
.
It is important to remember, however, that, due to the nonlinear character of the problem,
the superposition of different load cases is not possible. The analysis has to be performed
by a realistic combination of the applied loading multiplied by a scaling multiplier called
the
load factor
, which has to be kept above a certain safety limit (e.g., 1.75 or 1.5). In addition,
initially a linear analysis needs to be performed to obtain the variables of the fundamental









Search WWH ::

Custom Search