Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
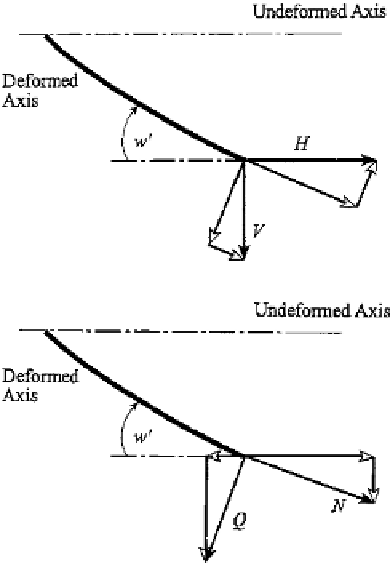
FIGURE 11.6
Transformation of forces aligned along the undeformed
axes with components along axes for the deformed bar.
FIGURE 11.7
Transformation of forces aligned along the deformed
axes with components along axes for the undeformed
bar.
to the usual stress resultants, fictitious forces are introduced that are conjugate to the di-
rections of the displacements in the sense that they perform work together. Assume small
rotations between the two axes so that sin
w
≈
w
≈
w
w
≈
In the frame-
work of the theory of second order, the linear transformation of the stress resultants
H
and
V
into components
N
and
Q
with respect to the deformed axes is given by (Fig. 11.6).
tan
and cos
1
.
w
+
w
w
N
=
H
cos
V
sin
or
N
≈
H
+
V
(11.7)
w
+
w
w
+
Q
=−
H
sin
V
cos
or
Q
≈−
H
V
In matrix notation, with the addition of the moment,
N
Q
M
w
w
cos
sin
0
H
V
M
=
w
w
−
sin
cos
0
(11.8)
0
0
1
The transformation of the stress resultants
N
and
Q
of Fig. 11.7 into components
H
and
V
along the axes corresponding to the undeformed bar is
w
−
w
w
H
=
N
cos
Q
sin
or
H
≈
N
−
Q
(11.9)
w
+
w
w
+
V
=
N
sin
Q
cos
or
V
≈
N
Q
In matrix notation
w
w
H
V
M
cos
−
sin
0
N
Q
M
=
w
w
sin
cos
0
(11.10)
0
0
1








Search WWH ::

Custom Search