Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
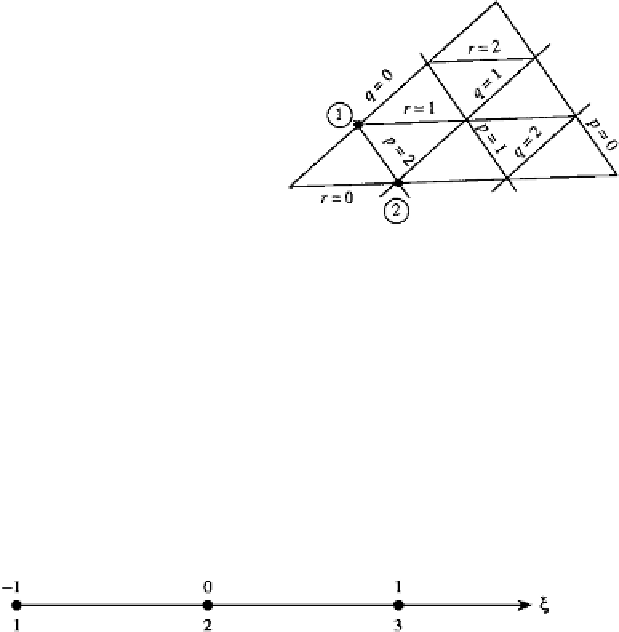
FIGURE P6.13
3
2
L
1
Hint:
N
2
(
L
1
)
=
(
3
L
1
−
1
)
,N
1
(
L
3
)
=
3
L
3
,N
1
(
L
2
)
=
3
L
2
,N
0
(
L
2
)
=
N
0
(
L
3
)
=
1
9
9
Answer:
N
1
=
2
L
1
L
3
(
3
L
1
−
1
)
,N
2
=
2
L
2
L
1
(
3
L
1
−
1
)
6.14 Construct the interpolation function for the element shown in Fig. P6.14. The interpo-
lation should be such that
=−
w
(ξ )
|
ξ
=
ξ
2
.
w(ξ)
=
N
1
w
+
N
2
w
+
N
3
θ
+
N
4
w
3
,
where
θ
1
2
2
2
1
2
2
3
1
2
2
3
3
,N
4
1
2
2
3
Answer:
N
1
=
(ξ
−
ξ
)
,N
2
=
1
+
(ξ
+
ξ
)
,N
3
=
ξ
−
ξ
=
(ξ
+
ξ
)
FIGURE P6.14
6.15 Suppose we have a structure as shown in Fig. P6.15a where a beam is connected to
a plane stress thin plate undergoing in-plane deformation. Beam and plane stress
plate elements of thickness
t
are to be used to analyze this structure. At the inter-
section between the beam and the plate, a transition or “blending” element of the
form of Fig. P6.15b can be employed. Obtain the
B
matrix for this element, where
k
i
aht
0
0
B
T
EB
d
=
ξ
d
η.
Hint:
The displacements in the element can be
h
2
η
u
x
=
N
1
u
x
1
−
N
1
θ
1
+
N
2
u
x
2
+
N
3
u
x
3
,
u
y
=
N
1
u
y
1
+
N
2
u
y
2
+
N
3
u
y
3
1
2
1
4
1
4
where
N
1
=
(
1
−
ξ)
,N
2
=
(
1
+
ξ)(
1
−
η)
,N
3
=
(
1
+
ξ)(
1
+
η)
and
D
u
is given
in Example 6.1.
6.16 Construct the stiffness matrix for a two-node beam element with shear deformation
effects taken into account. Use
k
i
=
1
0
B
T
EB
d
ξ.
Hint:
Use linear interpolation shape functions for both the deflection and the
rotation.









Search WWH ::

Custom Search