Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
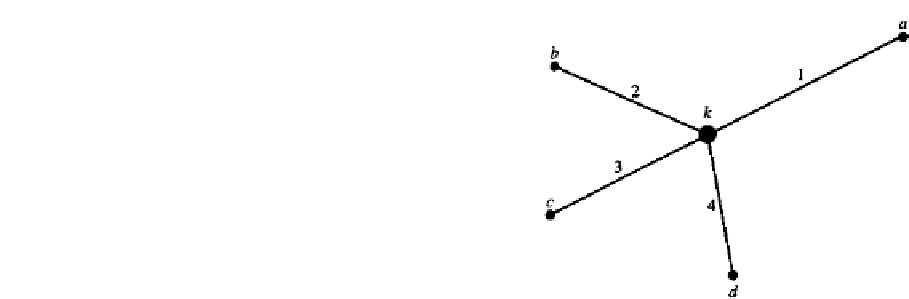
FIGURE 5.11
Node
k
with four elements.
If nodes
a
,
b
,
c
, and
d
as well as node
k
, are considered, the compatibility conditions
would appear as
.
.
.
.
v
a
v
k
...
v
b
v
k
...
v
c
v
k
...
v
d
v
k
I
v
1
a
1
.
.
.
.
V
a
I
···························
.
...
...
.
.
.
V
b
I
v
2
a
2
.
.
.
.
I
···························
.
...
...
=
=
V
c
=
V
(5.34)
.
.
.
I
v
3
...
.
.
.
.
a
3
...
V
d
I
···························
.
.
.
.
V
k
I
v
4
a
4
.
.
.
.
I
v
a
V
where
I
is a unit diagonal matrix and, for example,
0I000
0000I
a
2
=
is a submatrix of
a
.
In general, for a system with
M
elements, in which
v
i
contains all element nodal dis-
placements of element
i,
a
i
is formed for all nodes of element
i
, and
V
includes all system
displacements.
=
v
1
v
2
v
M
a
1
a
2
a
M
V
(5.35)
=
v
aV
The matrix
a
, which is given many labels such as
global kinematic, connectivity, locator
,or
incidence matrix
, contains information designating which element is connected to which







Search WWH ::

Custom Search