Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
References
Hetenyi, M., 1946,
Beams on Elastic Foundation
, University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor, MI.
Pestel, E. and Leckie, F., 1963,
Matrix Methods in Elastomechanics
, McGraw-Hill, NY.
Pilkey, W.D., 1994,
Formulas for Stress
,
Strain, and Structural Matrices
, Wiley, NY.
Pilkey, W.D., 2002,
Analysis and Design of Elastic Beams, Computational Methods
, Wiley, NY.
Pilkey, W.D. and Chang, P.Y., 1978,
Modern Formulas for Statics and Dynamics
, McGraw-Hill, NY.
Pilkey, W.D. and Pilkey, O.H., 1986,
Mechanics of Solids
, Krieger Publishers, Melbourne, FL.
Wunderlich, W., 1967, On the analysis of shells of revolution by transfer matrices,
Ing.-Arch.
, No. 36,
pp. 262-279.
Wunderlich, W., 1966, Calculation of transfer matrices applied to the bending theory of shells of Revo-
lution, Proc. Int. Symposium The Use of Electronic Digital Computers in Structural Engineering,
Newcastle upon Tyne.
Zurm uhl, R. and Falk, S., 1986,
Matrizen and ihre Anwendungen, Numerische Methoden, Teil 2
, 5th ed.,
Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Problems
Stiffness matrices
4.1 Several stiffness coefficients for a beam were found in Section 4.4.1 using a direct
evaluation procedure. Complete the direct evaluation of the stiffness coefficients for
a beam using the configurations of Fig. 4.7.
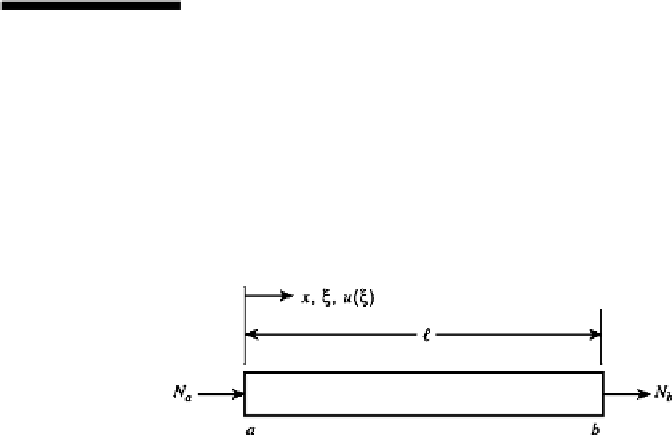
4.2 Find the stiffness matrix for an extension bar element (Fig. P4.2) using the approximate
series approach. Begin with the series
u
(ξ )
=
u
1
+
u
2
ξ
,
where
ξ
=
x
/.
FIGURE P4.2
Answer:
See the stiffness matrix for extension in Example 4.1.
4.3 Repeat the previous problem, except add a new DOF at the point which lies halfway
between a and b, and use a quadratic series
2
u
(ξ )
=
u
1
+
u
2
ξ
+
u
3
ξ
Answer:
7
−
81
EA
3
k
i
=
−
8 6
−
8
1
−
87
4.4 Derive the 2
×
2 stiffness matrix of the stepped truss element (extension bar) shown
in Fig. P4.4.











Search WWH ::

Custom Search