Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3.36 A cantilevered beam of length
L
and of rectangular cross section is loaded at the free
end with a concentrated force
P
. Determine the maximum deflection produced by
(a) bending
(b) the additional deflection caused by shear deformation.
PL
3
PL
k
s
GA
3.37 Solve Problem 3.11 using Castigliano's theorem, part I.
3.38 Determine the effect of shear deformation on the ma
xim
um deflection of a simply
supported beam of length
L
with a concentrated force
P
at
x
Answer:
w
max
=
w
bending
+
w
shear
=
3
EI
+
=
L
/
2.
PL
3
PL
4
k
s
GA
Answer:
w
max
=
w
bending
+
w
shear
=
48
EI
+
Reciprocal Theorems
3.39 Suppose a cantilevered beam of length
L
is loaded with a linearly varying distributed
force beginning with magnitude 0 at the free end and increasing to magnitude
p
0
at
the fixed end. Use Betti's reciprocal theorem to find the deflection at the free end (
a
)
and at the midspan (
b
).
p
0
L
4
01276
p
0
L
4
Answer:
w
a
=
/(
30
EI
)
,
w
b
=
0
.
/
EI
3.40 Consider a uniformly loaded (magnitude
p
0
) beam (length
L
) with one end fixed and
one end simply-supported. Use Betti's reciprocal theorem to calculate the deflection
at
L
/
2.
p
0
L
4
Answer:
/(
192
EI
)
3.41 For a cantilevered beam with a concentrated force
P
at the free end, use Maxwell's
theorem to calculate the deflection at
x
=
2
L
/
3 from the fixed end, where
L
is the
beam length.
14
PL
3
Answer:
w
=
/(
81
EI
)
=
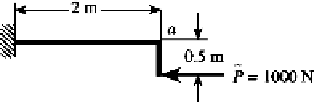
3.42 Calculate the vertical displacement of point
a
of the structure of Fig. P3.42. Let
E
200 GN/m
2
,
I
=
6000 cm
4
. Use Maxwell's reciprocal theorem.
FIGURE P3.42
w
=
.
Answer:
0
0833 mm.
a
3.43 Use Maxwell's theorem to find the midspan deflection of the beam described in
Problem 3.40.















Search WWH ::

Custom Search