Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.7 A compositional
plot of clinopyroxenes from
Vulsini, a leucite phonolite,
b trachyte, and c a plot of
clinopyroxenes from Vulsini
rocks in a pyroxene
quadrilateral (after Barton
et al. 1982)
leucite
phonolites
trachyte
(a)
(b)
Hd
Di
(c)
Fs
En
pyroxenes in pumice and scoria fragments are salites with consistently higher Ti
and Al than coexisting phenocrysts. The larger pyroxene crystals exhibit weak
sector or patchy zoning and rarely concentric zoning. Many diopside crystals with
fluid inclusions are deeply embayed in dark brown glassy groundmass.
Zoning in clinopyroxene is common in Vico lavas (Perini and Conticelli 2002).
The pyroxenes are ubiquitous micro-phenocrystal phase in Vico lavas (Cundari
1975), and sometimes they may be 1/2 cm long along the c-axis. In a conventional
plot of Ca
[Fe(total) + Mn], pyroxene compositions plot within the salite
domain, and display a general Fe-enrichment trend parallel to the diopside-he-
denbergite join. The distribution of Ti, relative to Al in co-existing core and rim
compositions generally show contrasting trends, suggesting complex history of
multiple equilibration in the pyroxene-liquid relationship. This may be in
Mg
-
-
uenced
by temperature and/or f(H
2
O)
fluctuation during the crystallization of pyroxene,
which contains up to 6.91 mol% CaFeSi
2
O
6
, variable amounts of CaAl
2
SiO
6
(5.7
13.9 mol%), small amounts of acmite (1.2
3.8 mol%) and up to 2.5 mol%
-
-
CaTiAl
2
O
6
molecule in solid solution.
Clinopyroxenes from leucite tehprites, phonotephrites, phonolites and foidites
from Alban Hills (Italy) are mainly phenocrysts in the post-caldera samples (Auri-
sicchio et al. 1988). The phenocrysts are of two distinct types: (1) normally zoned
variety exhibiting green to colourless core and dark green rim, containing inclusions
of opaques and (2) the reversely zoned crystals displaying a green core encircled by a
light green rim. The composition of phenocrysts with light green to colourless
pyroxene displays enrichment of Al, Fe
t
and Ti form the core to the rim and con-
comitant depletion inMg and Si. In the reversely-zoned crystals, a rim is characterised
by an increase of Si andMg andTi. depletion of Al, Fe
t
andTi. Ti. In a conventional pyroxene
quadrilateral, core compositions plot within the diopside field or above the diopside-
hedenbergite join. Cores of clinopyroxenes display reverse zoning. The pyroxenes are
of two different varieties (either diopside or fassite). The K-rich rocks of Hoch Eifel
(Germany) contain fassites (Huckenholz 1973). Duda and Schminke (1985) thought










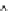

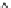








Search WWH ::

Custom Search