Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
1000
1000
100
100
10
10
RB-53 lc-ba, Erkeshan
4342, ol-lc, E.African Rift
Ave, lc-ba, Vulsini, Italy
155, ol-lc, Mexico
DZ-4 ol-lc, Keluo
G-1a lc-ba, Keluo
MH-1 trba, Keluo
Ba
Th
1
1
K
Ta Ce Nd Sm Hf
Tb Yb
Ba Th
K
Ta Ce Nd Sm Hf Tb Yb
Y
Rb
U
Nb
La
Sr
P
Zr
Ti
Y
Ti
Rb
U
Nb
La
Sr
P
Zr
(c)
10000
1000
100
10
H-38 lc-ba, Wudalianchi
XN 7 AOB, NE China
Ave. OIB
Ave. lamproite, Smoky Butte
Ave. lamproite, Gaussberg
1
Hf
Tb
Yb
Ba
Rb
Th
K
Ta
Ce
Nd
Sm
P
U
Nb La
Sr
Zr
Ti
Y
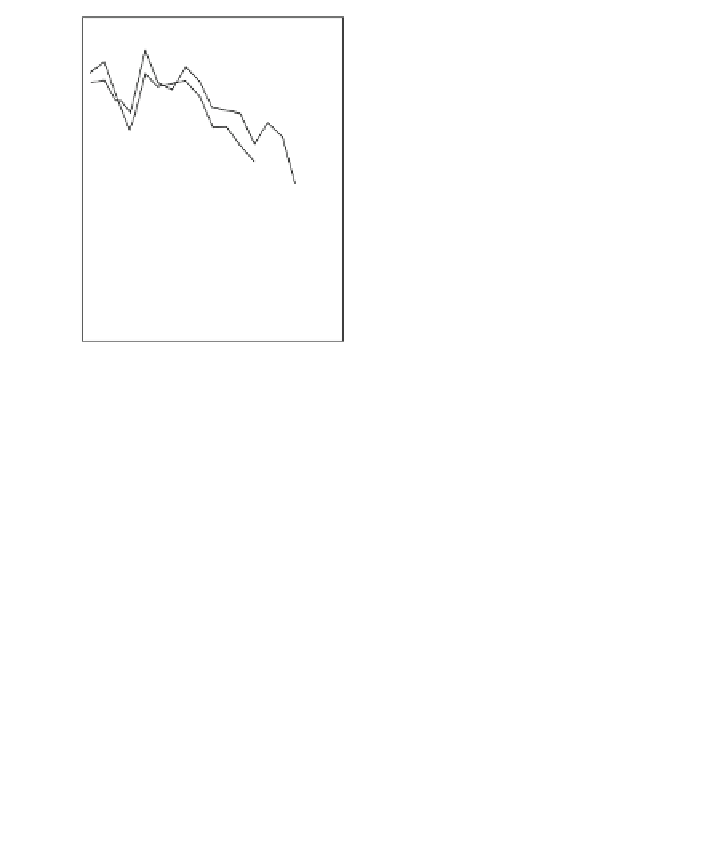
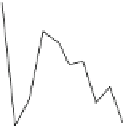
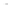
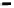
Fig. 5.20 Chondrite-normalized incompatible element plots for K-rich volcanic rocks from North
East China i.e. WEK volcanic rocks and other mantle-derived lavas (source Zhang et al. 1995)
All potassic rocks from northeast China have similar incompatible element
patterns (Fig.
5.20
a
c), the right side of which exhibit subparallel smooth curves
from La to Yb with slight Zr
-
Hf becoming more prominent with decreasing MgO
(e.g. from DZ-4 to G-la and MH-1). The sample MH-1 is distinct from the other
samples by its marked depletion of Nb
-
Ta in combination with the lowest K
2
O (3.5
wt%) and the highest SiO
2
(55 wt%) contents among the north-east China samples.
The slight
-
Ta displayed by north-east China
potassic rocks is quite different from East African potassic olivine leucitites in that
the rocks from the latter area present Nb
to moderate depletion in Nb
-
Ta enrichment similar to ocean island
basalts (OIB). The Chinese K-rich rocks distinguish themselves from those of the
-
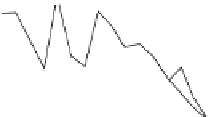











































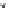







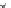









































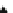











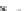





















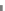

























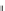














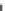





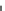
























































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search