Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Surfactant, cosolvent,
or water mixture
Polluted groundwater
removed and cleaned up
above ground
Ground surface
Groundwater
level
NAPL
Polluted groundwater
FIGURE 11.16
Example of in situ soil flushing. (From United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA),
A Citizen's
Guide to Soil Flushing
, EPA 542-F-01-0011, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, DC,
2001i.)
11.5.1 In Situ Soil Flushing
In situ soil flushing represents a modification to the traditional pump and treat system
and is employed to increase contaminant removal efficiency. With this method, water or
chemicals are pumped or percolated into saturated soil with the objective of flushing or
driving the contaminants to a location where they can be removed, usually by a pumping
well (Figure 11.16).
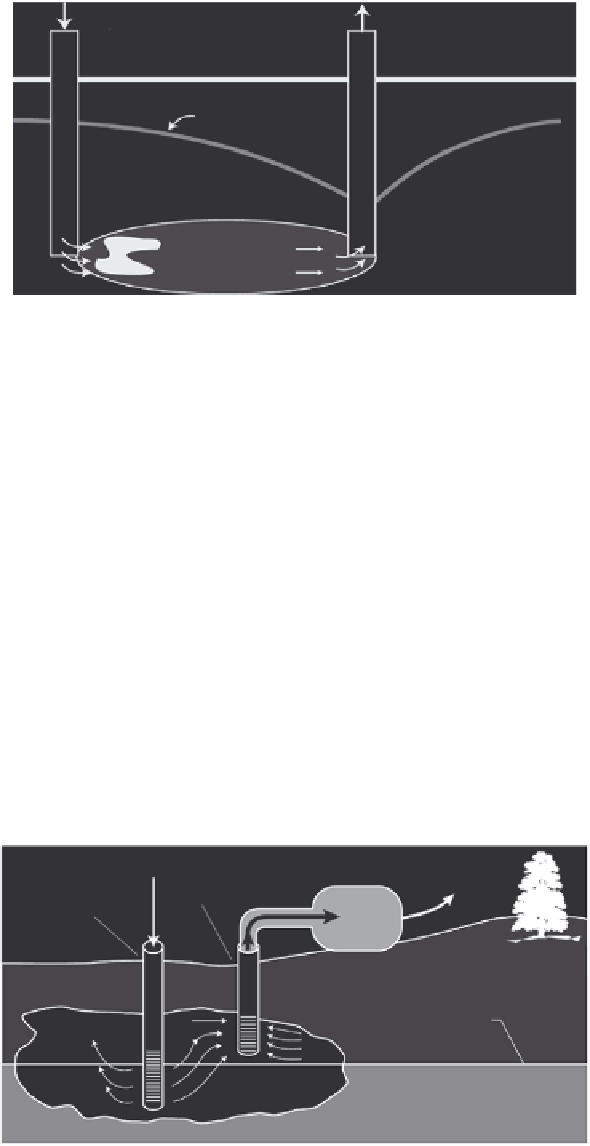
11.5.2 Air Sparging
Air sparging is an in situ groundwater remediation technology that uses injected air to
volatize contaminants in groundwater. As the injected air rises through the saturated zone
and reaches the unsaturated zone, the vapors containing the contaminants are removed
from the ground using a SVE system (Figure 11.17).
Air pollution
control equipment
Air in
Air injection well
(air sparging)
Extraction
well (SVE)
Water table
Pollution
FIGURE 11.17
Example air sparging system. (From United States Department of Energy,
Remediation Technologies Screening
Matrix and Reference Guide
, Version 4.0, Washington, DC, 2002.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search