Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
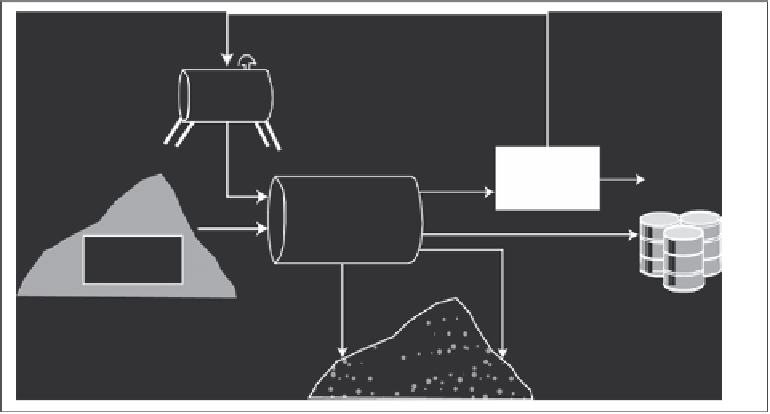
Water reused
Water and
detergent
Wash
water
Treatment
plant
Clean water
Scrubbing unit
Polluted
soil (sifted)
Polluted soil
to second cleanup
method or landfill
Clean soil
FIGURE 11.8
Example of soil washing. (From United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA),
A Citizen's Guide to
Soil Washing
, EPA 542-F-01-008, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, DC, 2001c.)
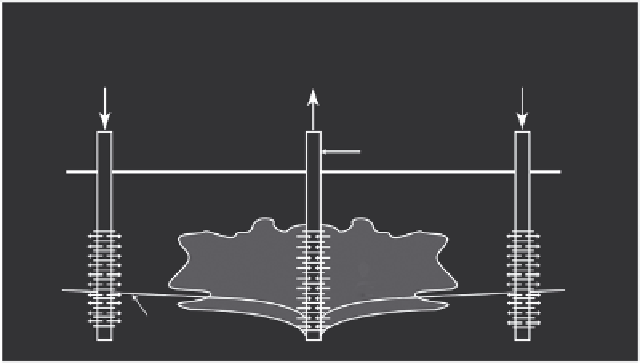
Steam injection
Gases and polluted water
removed and cleaned up
Steam
Steam
Collection well
Ground surface
Polluted
soil and
groundwater
Steam
Steam
Steam
Steam
Groundwater level
FIGURE 11.9
Example of in situ thermal treatment. (From United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA),
A
Citizen's Guide to In Situ Thermal Treatment
, EPA 542-F-01-0012, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response,
Washington, DC, 2001d.)
An added benefit of thermal technologies occurs when the heat destroys certain contami-
nants. In most cases, the added heat energy acts to evaporate the contaminants, and makes
collecting the contaminants using SVE much more efficient (Figure 11.9).
11.3.11 Ex Situ Thermal Treatment
Ex situ thermal treatment is similar to in situ thermal treatment with the key distinctions
being the contaminated soil is excavated and treated thermally at the surface. After treat-
ment, the soil is either returned into the ground or transported to a landfill.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search