Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
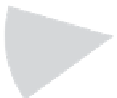
CRF
(GW)
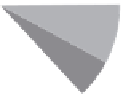
CRF
(SOIL)
Arsenic
Chromium VI
DNAPL
Arsenic
Mercury
Lead
LNAPL
PAHs
PCBs
DNAPL
Chlordane
DNAPL
Mercury
PCBs
Chromium VI
Others
Others
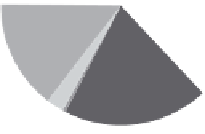
CRF
(AIR)
Chlordane
Chromium VI
PCBs
DNAPL
PAHs
Arsenic
Mercury
LNAPL
Lead
FIGURE 10.8
Pie charts of groundwater, soil, and air CRFs.
TABLE 10.15
Relative CRF Risk Rankings of Contaminants by Media
Compound
CRF
GW
CRF
SOIL
CRF
AIR
Chromium VI
Extremely high
Very low
Very high
DNAPL
High
High
Moderate
Arsenic
Low
Very low
Moderate
LNAPL
Very low
Very low
Moderate
Mercury
Very low
Extremely high
Very high
Lead
Very low
Very low
Low
PAHs
Extremely low
Very low
Very high
Chlordane
Extremely low
Very high
Very high
PCBs
Extremely low
Very high
Moderate
watershed within a variety of geological environments. Using as input the variables listed
in Table 10.6, early iterations of the stepwise procedure on the Rouge River watershed data
set retained extent of contamination and the total risk scores to explain remediation cost.
Examination of the distribution of the dependent and independent variables indicated
the data were positively skewed. After a logarithmic transformation, and the multiplica-
tion of the total risk scores by plume length, the River Rouge data set indicates a strong





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search