Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Particulate
pollutants in
atmosphere
Gaseous
pollutants in
atmosphere
Sources
Pollutants in
cloud water
and
precipitation
VOC
NO
x
Wet
deposition
Hg
NO
x
VOC
SO
2
Natural
Receptors
Anthropogenic
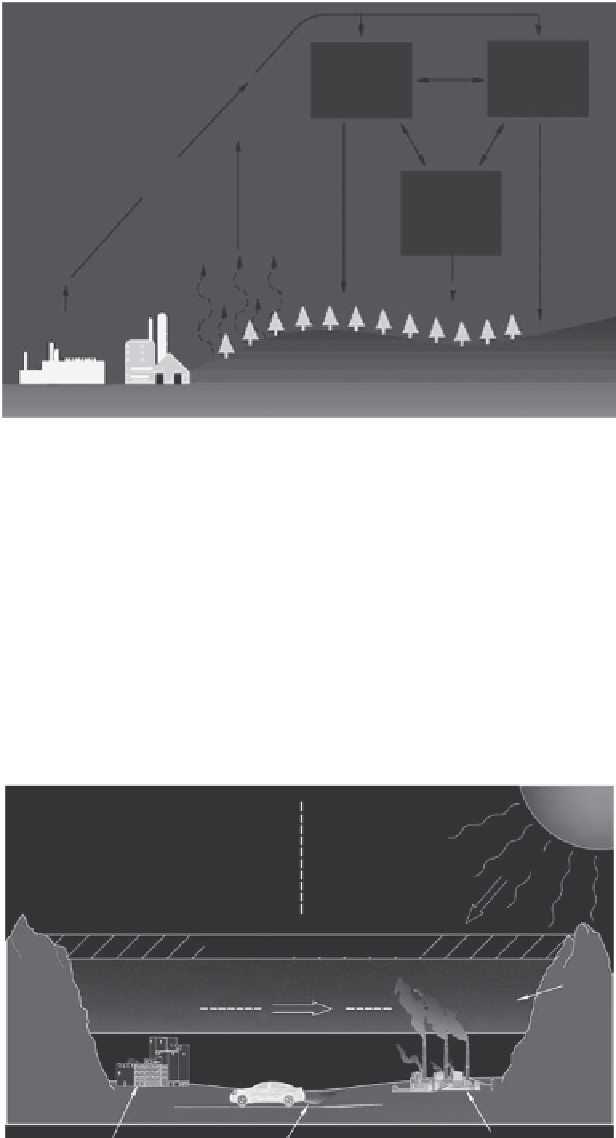
FIGURE 8.17
Process of wet and dry deposition of air contaminants. (From United States Environmental Protection Agency
(USEPA), What is acid rain? http://www.epa.gov/acidrain/what/index.html (accessed June 29, 2010), 2010.)
low-to-medium solubility, and low molecular weight. As a result of these chemical char-
acteristics, VOCs are common air, soil, and water contaminants (USGS 2006a; USEPA
2008a). Automobile exhaust contains VOCs. When combined with other common air pol-
lutants and sunlight, urban smog will form if atmospheric conditions are favorable—that
is, there is an ample supply of the combined sources of VOCs and other smog-forming
contaminants. This type of smog formation produces
photochemical smog
, and is shown
in Figure 8.18.
Step 1
Step 2
Accumulation of
air pollution
Smog
formation
Sunlight
Inversion (trapping pollutants)
NO
NO
2
O
3
SO
2
Smog
layer
Haze
CO
VOC
Industrial
facility
Vehicle exhaust
(cars, trucks, buses)
Electric power
generating plant
FIGURE 8.18
Formation of photochemical smog.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search