Database Reference
In-Depth Information
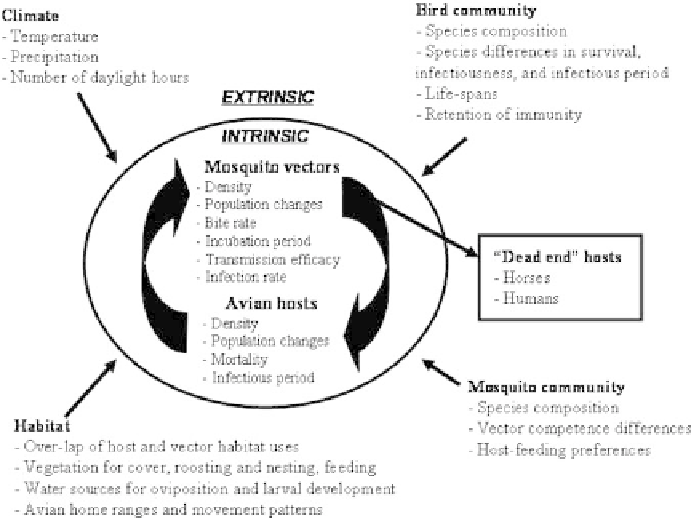
Fig. 12.1
In this chapter we build from a simple, population-dynamic SIR model of a con-
tagious disease to an indirectly transmitted arboviral disease model with explicit
population and seasonal dynamics. We use these models to qualitatively explore
how host and vector natural history and population dynamics might change predic-
tions as to how the disease outbreak will behave over time.
12.2 Susceptible-Infected-Resistant (SIR) Models
in Dynamic Populations
12.2.1 Model Structure and Behavior
3
established the value of including host population dynamics in models of bacterial
and viral disease outbreaks. They first incorporated changes in population density
to the classical SIR model, allowing for more ecologically based modeling of dis-
ease outbreaks in changing populations. While long used in a population-static form
3
Anderson, R.M. and R.M. May. Population biology of infectious diseases: Part I. Nature 1979a;
280: 361-367.