Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
PCA of the 4 sample 2 variables data set (v
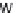
1
and v
2
are the 2 variables; s
1
, s
2
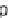
, s
3
and s
4
are the 4 samples)
Figure 4.1
Therefore, the main goal of PCA is decomposition of a data set into
principal components (PCs, i.e. LVs), which carry most of the information.
If the set of data points is represented in a two-dimensional coordinate
system, then LV (i.e. PC) is a line that passes in a direction where maximal
closeness to as many points as possible is achieved. In this way, most of
the data variation is captured and as little as possible of the information
is lost. The remaining variation is explained by the next LV, which is a
line orthogonal to the previous one.
Therefore, PCs maximize explained variance in the data set and a
constraint is put on their projection in terms of necessity of each successive
PC to be orthogonal to the previous one. The resulting model is bilinear
and represents the product of scores
T
and loadings
P
matrices, where
T

































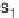



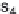



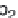

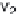

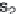

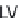
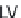


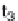


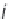








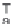

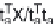












Search WWH ::

Custom Search