Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 7.4
Illustration of: (a) structured; and (b) unstructured grid
grid points with straight lines. There are two basic types of numerical
grids that differ in the way the grid points are connected: structured and
unstructured. A structured grid is characterized by regularity in the
connection, which means that every grid point is surrounded by the same
number of neighboring points. This is not the case with unstructured
grids, where every point is surrounded by a different number of neighbors
(Figure 7.4). A grid can also have both structured and unstructured parts,
as in the case of viscous fl ows, where a boundary layer can be structured
and the rest of the domain unstructured. The numerical algorithm should
be developed to suit the type of grid used. In most cases, numerical
algorithms written to use the structured grids cannot be used on
unstructured grids, while those written to use unstructured grids can be
applied on structured grids (Blazek, 2005; Sayma, 2009).
7.3 Application of CFD in
pharmaceutical technology
CFD has been recognized as a promising tool for the analysis and
optimization of various pharmaceutical unit operations, process
equipment, drug delivery devices, quality control equipment, etc.
Application of CFD methods in pharmaceutical product and process
development may lead to better process understanding, reduced number
of experiments, and reduced cost and time savings (Pordal et al., 2002;











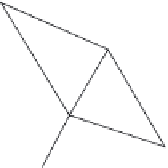






























Search WWH ::

Custom Search