Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
IVIVC plot for CBZ tablets in (a) water and (b) 1% SLS
(test IR tablets (▲); reference IR tablets (▲); test CR
tablets (●); reference CR tablets (●))
Figure 6.16
Another example considering identifi cation of the predictive
in vitro
dissolution of CBZ formulations was given by Zhang et al. (2011). The
authors reviewed a set of
in vitro
dissolution data obtained under different
conditions for different CBZ products, which were submitted to the
FDA, and made a selection of the representative
in vitro
dissolution
profi les, which were compared with the GastroPlus™ predicted CBZ
in
vivo
dissolution profi les in the fed and fasted states. The data collected
demonstrated that
in vitro
dissolution of CBZ from the IR suspension,
conducted in 900 mL water using USP Apparatus 2 with a rotation speed
of 50 rpm, was slower than the simulated
in vivo
dissolution in the fed
state but faster than
in vivo
dissolution in the fasted state, indicating that
the employed
in vitro
dissolution test conditions for CBZ IR suspension
could not be considered biorelevant (Figure 6.17a). In the case of the
CBZ IR tablet,
in vitro
dissolution profi les obtained in 900 mL media
containing 0.1% SLS, using USP Apparatus 2 with paddle speed of
75 rpm, were close to the
in vivo
dissolution in the fed state (Figure 6.17b).
For the CBZ XR tablet, the dissolution profi le obtained in 900 mL buffer
(pH 1.1, 4.5, and 6.8), using USP Apparatus 1 at 100 rpm, correlated
well with
in vivo
dissolution under fed conditions (Figure 6.17c). For the
XR capsule, the best relationship between
in vitro
and
in vivo
data under
both fasted and fed conditions was achieved with the dissolution profi le
obtained in 900 mL buffer containing 0.1% SLS using USP Apparatus 2
at 50 rpm (Figure 6.17d). In addition, the repeated simulations performed
for fasted state, using the same solubility as for the fed state, gave an
almost identical
in vivo
dissolution rate to that obtained under the fed
state, indicating that the differences in
in vivo
dissolution rates between



















































































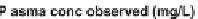



















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search