Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
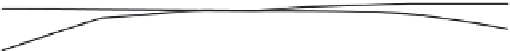
Parameter sensitivity analysis: oral bioavailability
(%) as a function of reference solubility at pH 6.5
(mg/mL) (dark squares), and effective particle radius
(μm) (light squares) at a dose of 160 mg R1315
(reprinted from Kuentz et al., 2006; with permission
from Elsevier)
Figure 6.9
selected for phase I clinical studies, leading to considerable resources
being saved.
Dannenfelser et al. (2004) reported a case where PSA analysis revealed
that drug solubility and particle size clearly infl uenced oral absorption of
a poorly soluble drug. Additional PK studies in dogs revealed that
solid dispersion containing water soluble polymer with a surface
active agent showed comparable bioavailability with the cosolvent-
surfactant solution (considered to be 100% bioavailable), both of
which showed 10-fold higher bioavailability than the dry blend of
micronized drug with microcrystalline cellulose. Thus, a capsule
containing solid dispersion formulation was selected for clinical
development.

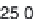
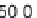
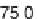
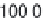
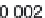


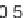

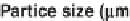




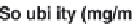





























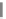
























Search WWH ::

Custom Search