Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Organization of the neural network consisting of an
input layer, one hidden layer, and an output layer (all
neurons are fully connected)
Figure 5.2
multiplied by their corresponding weights and converted to the output by
an activation (transformation) function in the following way:
[5.1]
where
w
pq
is the weight of the connection between the neuron (unit),
q
in
the current layer to unit
p
in the previous layer, and
x
p
is the output value
from the previous layer (it is the input value for the neuron in the current
layer).
Then, an activation function is applied, sigmoid, for example:
[5.2]
where α is a parameter relating to the shape of the sigmoid function and
f
(
y
q
) is applied to the following layer as an output value (it then becomes
x
p
). Nonlinearity of the sigmoid function is strengthened with an increase
in α (Takayama et al., 2003). According to the value of α, the function
changes from nearly linear to a strong nonlinear function, such as a
step function (Ichikawa, 2003). Other activation functions can be used,
such as piecewise linear functions, step functions, Gaussian functions,








































































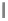





Search WWH ::

Custom Search