Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
V
φ
3
D
3
D
1
D
2
V
2
φ
1
V
1
φ
2
φ
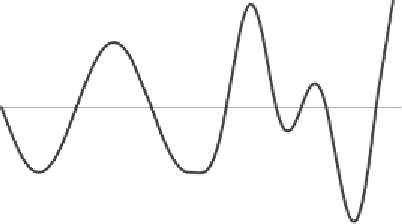
Figure 2.4. Example of two potentials and resulting domains of the steady-state
stochastic dynamics of
φ
(
t
).
φ
=
φ
st
<
0and
d
f
1
(
φ
)
d
1isstableif
f
1
(
φ
st
)
=
0, whereas it is unstable if
f
1
(
φ
st
)
=
0and
φ
φ
=
φ
st
>
d
f
1
(
φ
)
0.
The characteristics of the stationary points can be easily represented by the poten-
tials
V
1
(
d
φ
φ
)and
V
2
(
φ
), defined as
d
V
1
(
φ
)
d
V
2
(
φ
)
f
1
(
φ
)
=−
,
f
2
(
φ
)
=−
;
(2.38)
φ
φ
d
d
the stable (unstable) stationary points correspond to the minima (maxima) of the
potentials. The dynamics of
φ
can then be represented as those of a particle moving
φ
along the
axis driven by the switching between the two potentials. Thus the particle
remains trapped between any pair of stable points [minima of the potentials
V
1
(
φ
)and
V
2
(
φ
)] that are not separated by an unstable point [i.e., a maximum of either
V
1
(
φ
)or
V
2
(
)]. These pairs of minima define the domain of the steady-state pdf.
To demonstrate this rule for the determination of the extremes of the domains in
which
φ
fluctuates at steady state, we can consider the example shown in Fig.
2.4
and assume that the initial condition (at time
t
φ
=
0) of the process corresponds to
position 1 on potential
V
1
(
φ
). At time
t
>
0 the particle starts moving downhill to its
right, along potential
V
1
(
2
,
the particle is at a certain position 2 (see Fig.
2.4
). At this point the particle will start
moving following potential
V
2
(
φ
) (dashed line). When the noise randomly switches to
) (solid line), i.e., like a particle released in position
3. From position 3 the particle can move only to its right, regardless of whether the
noise switches to
φ
1
. Thus it will necessarily enter (and remain confined within) the
domain indicated by
D
2
. In fact, once the particle enters
D
2
, it necessarily remains
trapped inside it, and
D
2
becomes the domain of the steady-state pdf. Notice that the
jump from position 2 to 3 could have occurred before the maximum of the
V
2
(
)
potential was reached. In this case the particle would have been attracted to the
D
1
φ








Search WWH ::

Custom Search