Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
key.environmental.processes,.such.as.the.fate.and.transport.of..contaminant..metals..
In. order. to. probe. the. 3D. structure. of. this. interface,. hard. x-ray. scattering. and.
spectroscopic. techniques,. including. crystal. truncation. rod. diffraction. and. x-ray.
relectivity,
86-88
.are.used.to.determine.the.identity.and.ordered.arrangement.of.atoms.
at. the. surface.. In. particular,. the. arrangement. of. water. and. other. aqueous. species.
on. metal. oxide. surfaces. can. be. determined. with. high. accuracy.. One. drawback. of.
these.hard.x-ray.scattering.techniques,.however,.is.the.limited.sensitivity.to.(1).low.
Z
. elements,. such. as. hydrogen,. due. to. their. weak. scattering. power,. and. (2). poorly.
ordered.interfacial.components,.such.as.weakly.bound/disordered.sorbates.and.phy-
sisorbed.water..Quantum.mechanics-based.methods,.such.as.the.DFT,.and.the.classi-
cal.mechanics-based.methods,.for.example,.molecular.dynamics,.are.used.to.provide.
complementary.and.predictive.models.for.interface.structure.and.reactivity,.which.
may.then.be.used.to.guide.experimental.characterization.and.structural.analysis.
The.hydrated.α-Fe
2
O
3
.(0001).surface.possesses.a.unique.surface.termination.that.
was.recently.elucidated.with.the.help.of.DFT.calculations.and.ab.initio.thermody-
namics.
89
.Trainor.et.al..showed.that.two.surface.terminations,.(HO)
3
-Fe-Fe-R.and.
(HO)
3
-Fe-H
3
O
3
-R.are.observed.to.coexist.under.H
2
O.partial.pressures.greater.than.
10
−4
. Torr. in. a. roughly. 2:1. ratio.. These. two. surface. terminations. may. coexist. in. a.
single.domain,.giving.an.overall.surface.stoichiometry.of.(HO)
1.2
-Fe
0.4
-H
1.2
O
3
-R,.or.
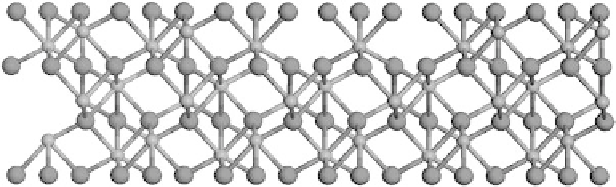
exist.as.two.separate.linked.domains..Figure.7.7.shows.a.schematic.of.the.α-Fe
2
O
3
.
(0001).surface,.with.a.partial.occupancy.of.the.layer-2.Fe.cations.
Ab.initio.thermodynamics.was.then.used.in.conjunction.with.DFT.to.approximate.
the.surface.free.energies.of.these.and.other.surface.terminations.of.α-Fe
2
O
3
.(0001).
89
.
These. studies. predicted. that. (HO)
3
-Fe-H
3
O
3
-R. is. indeed. the. most. stable. surface.
termination.under.conditions.of.equilibrium.with.gas.phase.H
2
O.and.O
2
..However,.
since.natural.surfaces.come.into.contact.with.liquid.water.rather.than.the.gas.phase.
water.models.commonly.used.in.these.studies,.new.thermodynamic.models.for.treat-
ing.interfacial.water.in.contact.with.solid.surfaces,.including.solvation.and.entropy.
effects,.are.ripe.for.future.development.
The.structure.of.the.metal.oxide-water.interface.in.α-Fe
2
O
3
.(11
_
02).has.been.the.
subject. of. much. debate. by. experimentalists.
90-92
. On. one. hand,. the. heterolytic. dis-
sociation.of.water.into.H
+
.and.OH
-
.is.the.natural.irst.step.allowing.these.species.to.
FIGURE 7.7
Possible. “linked. domain”. model. for. the. hydrated. α-Fe
2
O
3
. (0001). surface.
(waters.not.shown)..Only.partial.occupancy.of.the.layer-2.Fe.cations.is.observed.experimen-
tally,.and.the.results.from.DFT.calculations.and.ab.initio.thermodynamics.are.consistent.with.
these. two. terminations. being. the. most. energetically. stable. at. the. oxygen. partial. pressures.
observed.under.environmental.conditions.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search