Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
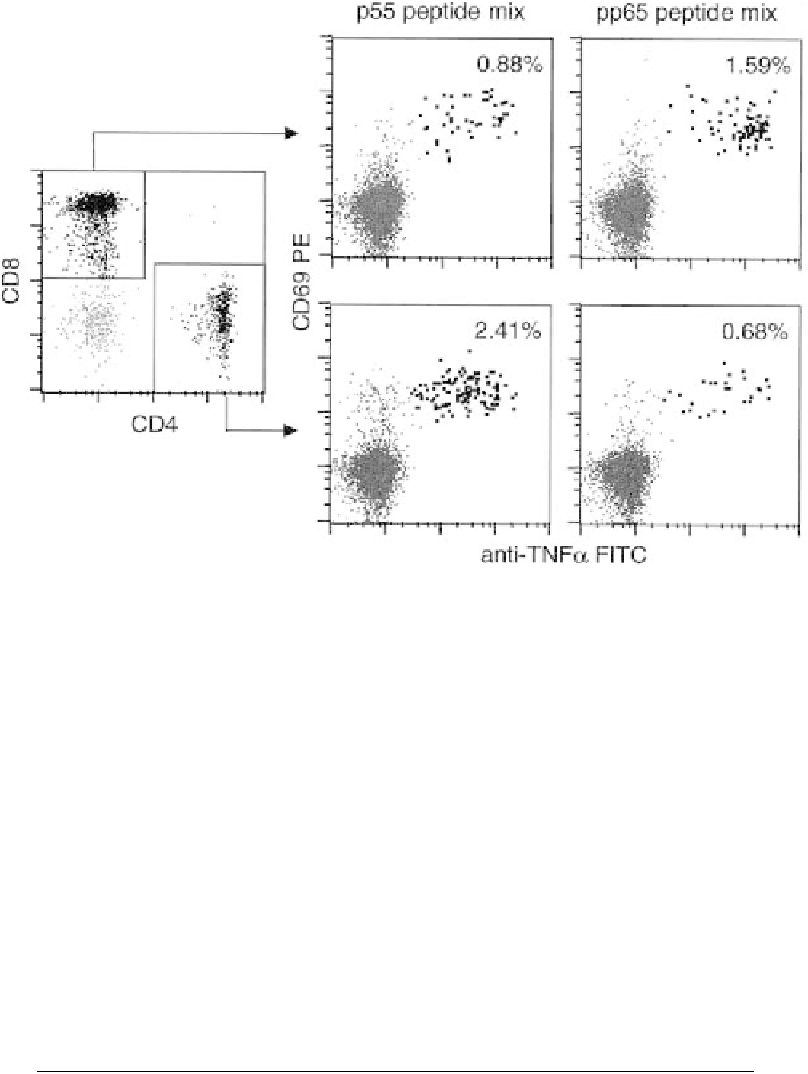
F i g u r e 18.1. Simultaneous detection of CD4
and CD8
T-cell cytokine responses to peptide
mixtures derived from sequences of p55 gag and pp65 protein subunits of HIV and HCMV. Whole
blood from an HIV and CMV seropositive donor was stimulated for 6 h using 15-mer overlapping
peptide mixtures shown at the top. CD8-gated (top row) and CD4-gated (bottom row) responses are
shown. Note that in this example the pp65 15-mer peptide mix stimulates a signi®cantly higher CD8
response than was observed for the CD4
T-cell response. In contrast, the HIV response was pre-
dominantly observed within the CD4
T-cell subset.
use of peptide-HLA class I tetrameric complexes with intracellular cytokine
staining to assess the functional heterogeneity of CD8
T cells. These inves-
tigators showed that the majority of circulating CD8
T cells speci®c for CMV
and HIV antigens are functionally active with regard to the secretion of antiviral
cytokines in response to antigen, although a subset of tetramer-staining cells was
identi®ed that secretes IFN-g and macrophage in¯ammatory protein (MIP)-
1beta but not TNF-a.
USE OF CYTOKINE FLOW CYTOMETRY TO MONITOR
VACCINE-INDUCED IMMUNE RESPONSES
Although new combinations of antiretroviral drugs have improved the quality
of life and length of survival of patients with HIV infection, it is clear these