Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
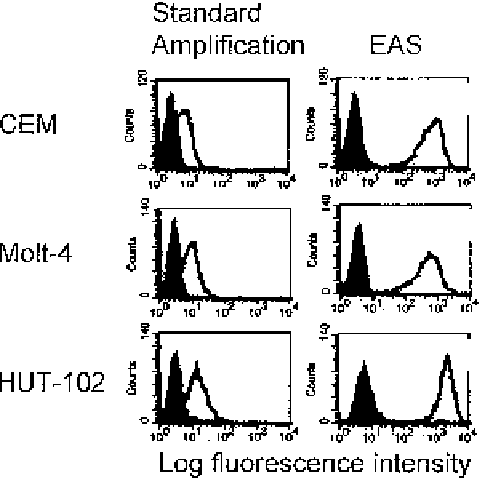
F i g u r e 17.1. The human T-cell tumor lines CEM, Molt-4, and HUT-102, were stained with 5 ng
of biotinylated control murine IgG1 (closed histograms) or 5 ng biotinylated anti-human CD5 (open
histograms). The panels on the right represent cells stained with standard ampli®cation procedures,
and the panels on the left represent cells stained with EAS.
that express CD5, gave similar results. The channel separation between control
and speci®c antibody peaks with standard ampli®cation was 6 channels for
Molt-4 cells and 12 channels for HUT-102 cells, whereas the channel separation
with EAS (normalizing the control peak at the same channel number) was 409
channels for Molt-4 cells and 940 channels for HUT-102 cells. Excellent ¯uo-
rescent signal enhancement has been obtained with every cell analyzed.
Moreover, we have tested antibodies to over 50 di¨erent molecules on vari-
ous cells including tumor lines grown in culture, neoplastic lymphocytic cells ex
vivo, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) ex vivo, and PBMC acti-
vated and cultured in vitro. In every case, we have obtained marked ampli®ca-
tion. The cell surface markers that we have analyzed include major histo-
compatibility complex (MHC) class I, MHC class II, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD6,
CD7, CD25, CD34, CD45, CD79b, CD122, CD132, Ig kappa light chain, Ig
lambda light chain, cytokine receptors, viral glycoproteins, and glycolipids,
among others.
We have also performed comparative analyses with dilutions of the primary
antibodies (Kaplan and Smith, 1999). These analyses suggested two important
points to us. First, EAS allowed us to observe cell-surface molecules at anti-
body amounts that could not be used to detect these molecules using other