Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
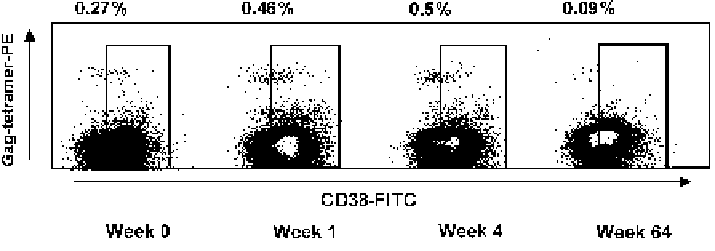
Figure 15.4. Freshly stained CD38
Gag-speci®c CD8
cells in PBMC isolated from an HIV-1-
infected patient receiving HAART. An initial increase in the frequency of activated antigen-speci®c
cells was observed in the ®rst 4 weeks of HAART and by 64 weeks was slightly above the detectable
threshold on the FACS.
1998) where there are data to show that lymphoid architecture improves (Gray
et al., 2000; Haase, 1999; Tenner-Racz et al., 1998; Zhang et al., 1999) and
there are increased CD4
T-cell responses to recall and neoantigens ( Valdez et
al., 2000). There are also data to show that the frequency of antigen-speci®c
responses in peripheral blood declines in response to HAART (Gray et al., 1999;
Kalams et al., 1999; Ogg et al., 1998, 1999a). It has been observed that there is
often an initial increase in the frequency of antigen-speci®c cells in the ®rst 4
weeks after initiation of HAART (Gray et al., 1999; Ogg et al., 1999a), where
these cells show increased surface expression of CD38, HLA-DR, and CD69
(Gray et al., 1999) compatible with possible e¨ector CTL function. Figure 15.4
shows a representative patient receiving HAART, where a signi®cant increase
in CD38
Gag-speci®c CD8
cells occurs in the ®rst week and thereafter de-
clines (Gray et al., 2000). After 1 year of treatment, the frequency of tetramer-
positive cells declined to levels marginally above the lower limits of detection by
¯uorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis. It is possible that the initial
increased frequency of these activated cells during the early treatment phase
re¯ects release of tissue-resident CTL into the circulation. Other studies have
shown that after the initial rise in tetramer positive staining, a steady decay of
tetramer-positive cells (median half-life of 45 days) continues for as long as
there is suppression of HIV replication (Ogg et al., 1999a). Collectively, these
data suggest that suppression of high levels of replicating HIV-1 during the
chronic stage of infection removes the stimulus required for maintaining HIV-
speci®c CD8
T cells. Hence, it is unlikely that HIV antigen-speci®c cells dur-
ing chronic infection are controlling viral replication. Conversely, recent data
have shown that provision of HAART at the time of seroconversion results in
maintenance of numbers and function of CD4
and CD8
antigen-speci®c T
cells (Oxenius et al., 2000).