Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
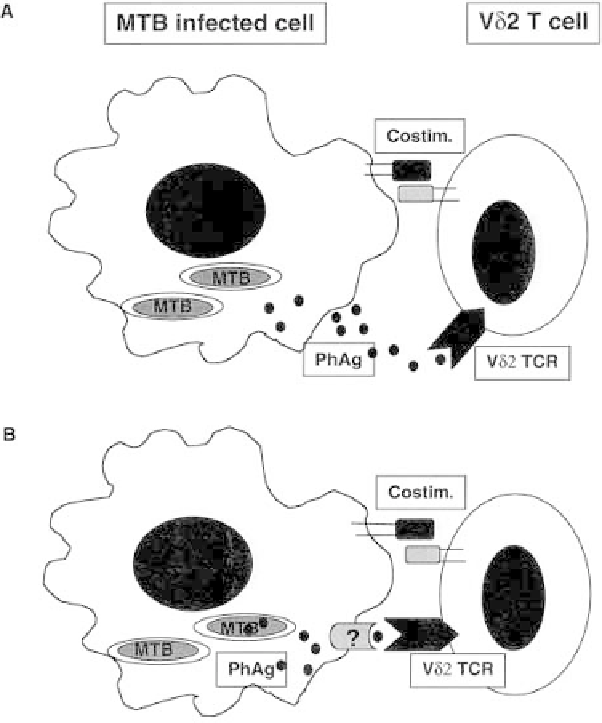
F i g u r e 8.1. Recognition of phosphoantigens by Vg9Vd2 T cells. Di¨erent models of phospho-
antigen recognition have been proposed based on studies with mycobacteria such as M. tuber-
culosis (MTB). (A) Phosphoantigens (PhAg) are secreted by intracellular MTB or originate as a
product of MTB breakdown. Once phosphoantigens escape the phagocyte, they interact directly
with the TCR (Vd2 TCR). In this case, recognition takes place without involvement of intracellular
processing or presentation by antigen-presenting cells (APC ). Upon interaction with TCR, hydro-
lysis of phosphate takes place and the gd T cell is activated (not shown). In this model, the role of
phagocytes is limited to providing costimulation (Costim.). (B) MTB is taken up by phagocytes and
after degradation inside phagosomes, phosphoantigens tra½c inside the cytoplasm. They become
stably associated with the surface of the APC, mediated possibly by an antigen-presenting molecule
(yet unidenti®ed ?) and interact with the gd TCR (Vd2 TCR). Hydrolysis of phosphate (P) from
the phosphoantigen takes place (surface processing) allowing optimal T-cell activation. Phagocytes
also provide costimulation (Costim.) in addition to a presenting molecule.