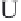Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
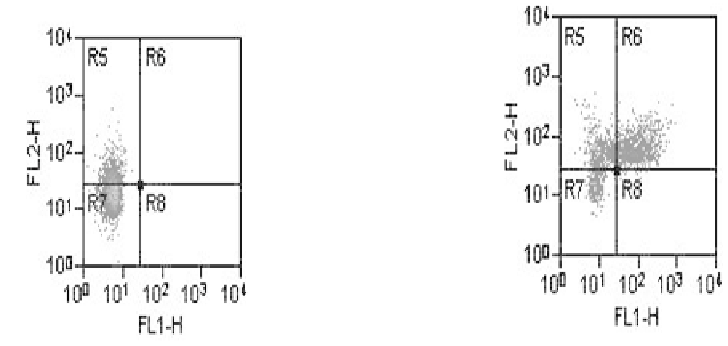
Figure 6.3. Intracellular Cytokine Assay.
been shown to generally correlate with CTL lysis. A related method is the JAM
test where radioactive labels like [
3
H]TdR, are used to label the target cells. The
amount of intact DNA retained by living cells is then measured by harvesting
the cells as in proliferation assay and measuring the amount of radiation in-
corporated into the intact DNA (fragmented DNA from dead cells is washed
through the ®lters and lost) using radioactive counters (Matzinger, 1991). The
drawback of these techniques is related to the di¨erences in the DNA frag-
mentation in target cells from the same and di¨erent subjects, the dependence
of this mechanism on the actual number of e¨ector cells used, and nonlinearity
of CTL killing ( Ratner and Clark, 1991). In addition, some cell types such as
resting ®broblasts have been shown to spontaneously release DNA during CTL
killing which may a¨ect the data.
Membrane Stability
These tests are aimed at measuring a breach in the plasma membrane of target
cells as a consequence of CTL killing. The hallmark of CTL killing is the lysis
of the target cells by either the perforin-dependent granule-exocytosis path-
way (Koopman et al., 1997) or the Fas/FasL pathways. This lysis leads to