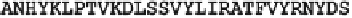Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Hamming distance
A
1: 01010010
|||||
2: 11010001
B
1: BIRD
||
2: WORD
D=3
12
D=2
12
Figure 6.
The Hamming distance is the number of exchanges necessary to turn one
string of bits or characters into another one (the number of positions not connected
with a straight line). It is assumed that the two strings are of identical length and
that no alignment is necessary. The exchanges in character strings can have different
costs, stored in a lookup table. In this case the value of the Hamming distance will
be the sum of costs, rather than the number of the exchanges.
Range of alignment
EIYEGKRYNLPTVKDQ-S
Mismatch
Gap
Figure 7.
A string similarity measure can be defined as a sum of costs assigned to
matches, replacements and gaps (insertions and deletions). The two strings do not
need to be of the same length. A string similarity measure between biological
sequences is a maximum value calculated within a range of alignment. The
maximum depends on the scoring system that includes a lookup table of costs, such
as the Dayhoff matrix, and the costing of the gaps.
The alignment used here is no longer unique, like in the case of a Hamming
distance, and there are different (arbitrary) ways to cost gaps (different cost factors for gap
opening and gap extension etc.). Establishing an alignment between two sequences consists
in maximizing a similarity measure given in equation [5]. This problem can be solved if in
addition to the formula of
S
we have a cost matrix for replacements and identities, or some
other lookup table that contains the similarity/distance values of the elements used in the
description. In the case of proteins, the cost factors of amino acid substitutions are included
in the well-known Dayhoff and BLOSUM matrices, and there are several established
strategies for costing the gaps - for recent reviews see (). The algorithm for finding a
maximal similarity between two longer sequences is an optimization problem. The actual
algorithms of similarity search are beyond our scope. The basic principle is mentioned in
section 3.5, and some examples are given in section x.x. There are number of
comprehensive reviews on this subject.
2.5 The rmsd distance for protein 3-D structures
A very popular quantity used to express the structural similarity of 3-D structures is the
root-mean-square distance (
rmsd
) calculated between equivalent atoms, defined as
¦
d
2
[6]
i
rmsd
i
N