Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
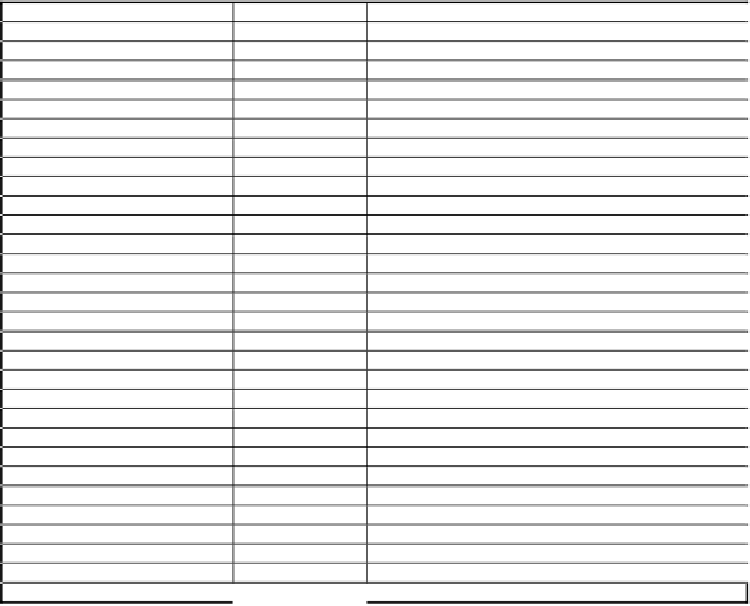
Table 4a.
Twenty-three SAND sequences identified in protoctista, fungi, plants and
invertebrates.
Organism
SAND identifier
Accession Number
Fungi
Gibberella zeae
GZ_SAND
EMBL:AACM01000298
Neurospora crassa
NC_SAND
SPTR:Q870Q4
Schizosaccharomyces pombe
SP_SAND
SPTR:Q10150
Eremothecium gossypii
EG_SAND
SPTR:Q75EA2
Aspergillus nidulans
AN_SAND
EMBL:EAA64925
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
SC_SAND
SPTR:P53129
Yarrowia lipolytica
YL_SAND
EMBL:CAG81815
Candida albicans
CA_SAND
*
Plasmodia
Plasmodium falciparum
PF_SAND
SPTR:Q8IDH2
Plasmodium yoelli trophy
PY_SAND
SPTR:Q7RL16
Slime mould
Dictyostelium discoideum
DD_SAND
EMBL:BJ377438 EMBL:C24407 EMBL:BJ330011
Nematodes
Caenorhabditis elegans
CE_SAND
SPTR:Q9B189
Caenorhabditis briggsae
CB_SAND
EMBL:AC084558
Insects
Drosophila melanogaster
DM_SAND
SPTR:Q9VR38
Apis mellifera
AM_SAND
REFSEQ:XP_396160
Anopheles gambiae
AG_SAND
SPTR:Q7Q176
Sea squirt
Ciona intestinalis
CI_SAND
EMBL:BW166332 EMBL:BW295692
Plants
Arabidopsis thaliana
AT_SAND
SPTR:Q9SKN1
Lycopersicon esculentum
LE_SAND
EMBL:BI927128 EMBL:BI930515 EMBL:AW222182
Glycine max
GM_SAND
EMBL:BE474111 EMBL:BM522384 EMBL:CA851897
Oryza sativa
OS_SAND
SPTR:Q94CS8
Triticum aestivum
TA_SAND
EMBL:AL826200 EMBL:CD896369
Saccharum officinarum
SO_SAND
EMBL:CA79484 EMBL:CA097914
Unfinished sequences for
C. albicans
was obtained from the NCBI
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST). The
S. cerevisiae
comprises 644 residues; our
analysis would indicate that an intron is present in this prediction.
In this chapter, we use these protocols to study a gene, first reported as open reading
frame G2889, on chromosome VII of
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
. At the time, the translated
ORF G2889 showed no significant sequence similarity to other proteins in the databank
[23]. Three years later, a homologue was identified from an analysis of the plasminogen
related growth factor receptor 3 (PRGFR) gene locus in
Fugu rubripes
(FR_SAND1; Table
4). The homologue was named SAND because it is neighbouring a PRGFR gene that is an
orthologue of SEA [24].
Additional SAND homologues were found as eukaryotic genome sequences, such as
Caenorhabditis elegans
,
Drosophila melanogaster
and
Arabidopsis thaliana
, became
available [25]. Whilst one SAND homologue was found in each of these genomes, two
copies were identified from searches of the then unassembled human genome [25]. In
addition, the protein SAND (known as Mon1p in yeast) was shown to function at the
tethering/docking stage of vesicle/vacuole fusion as a critical component of the vacuole
SNARE complex [26, 27]. In this chapter, we describe a multidisciplinary bioinformatics
approach by using comparative genomics, structure prediction [28] and phylogenomics
[29], to shed light on the possible structure and function of various members of the SAND
protein family. Resources for various protein structure prediction techniques are described