Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
extensively by quantitatively using three-dimensional structures and by re-examining the
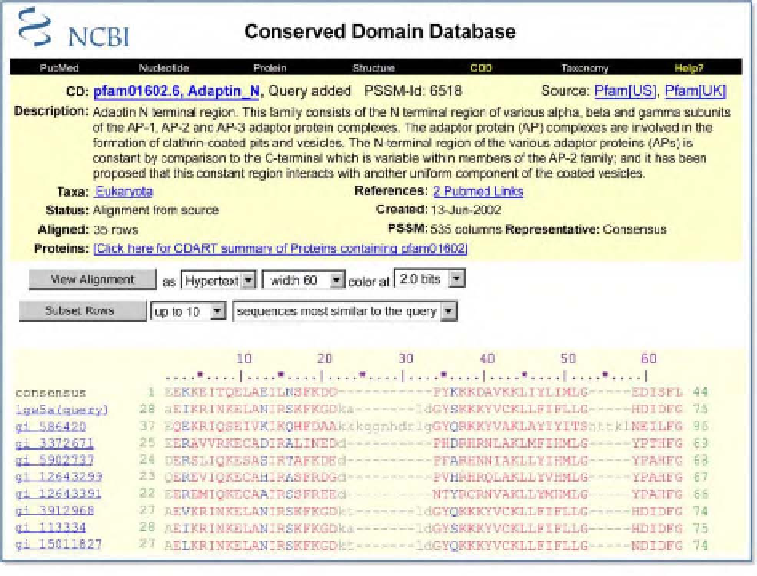
Figure 4: CD summary page.
The
top
of the page serves as a header and reports a variety of identifying
information, including the name and description of the CD, other related CDs with links to their summary
pages, as well as the source database, status, and creation date of the CD. A taxonomic node link (
Taxa:
)
launches the Taxonomy Browser, whereas a Proteins link (
Proteins:
) uses CDART to show other proteins
that contain the CD.
Below
the header is the interface for viewing the CD alignment, which can be done
either graphically with Cn3D (if the CD contains a sequence with structural data) or in HTML, text, or
mFASTA format. It is also possible to view a selected number of the top-listed sequences, sequences from
the most diverse members, or sequences most similar to the query. In addition, users may now select
sequences with the NCBI Taxonomy Common Tree tool. The
lower portion
of the page contains the
alignment itself. Members with a structural record in MMDB are listed first, and the identifier of each
sequence links to the corresponding record.domain extent. In addition, CDD curators annotate conserved
functional residues,
ligands, and co-factors contained within the structures. They also record evidence for
these sites as pointers to relevant literature or to three-dimensional structures
exemplifying their properties. These annotations may be viewed using Cn3D and thus
provide a direct way of visualizing functional properties of a protein domain in the
context of its three-dimensional structure. (See Appendix 3 and Figure 7.)