Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
sheets are misaligned [15]. The anti-parallel conformation is therefore more favoured,
however the presence of bulky or branched sidechains such as valine and isoleucine can
favour the formation of parallel
-sheets which accommodate these sidechains more easily
[16]. The beta sheet postulated by Pauling and Cory [13] was planar an example of which
can be seen in glutathione reductase (figure 8) however this is rarely seen and most sheets
have a right-handed twist when viewed in the direction of the polypeptide chain (figure 9)
due to intra- and inter-chain interactions involving the sidechains [15] [16]. The twist tends
to be greater in anti-parallel sheets, which are more flexible than parallel sheets and can
sometimes be exaggerated into a coil.
β
-sheets can also change directopn by ~90
o
with the
insertion of a residue with the polyproline II conformation (
β
β
-bend) or the
α
- conformation
(
β
-bulge) [17]
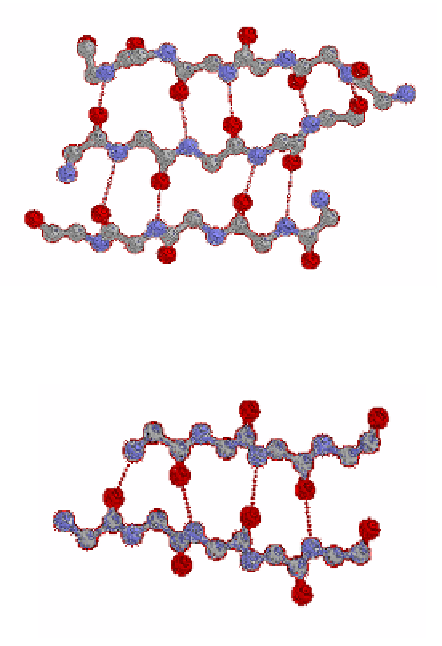
Figure 6. RASWIN ball and stick model of an anti-parallel β-sheet showing
hydrogen bonds between strands.
Figure 7. RASWIN ball and stick model of a parallel β-sheet showing hydrogen
bonds between strands.
2.3 Loops and hydrogen-bond stabilised turns
About one third of the residues in globular proteins are found in turns and loops, which
reverse the direction of the polypeptide chain, a prerequisite for the formation of a compact
globular structure. Turns are normally located at the surface of a protein, therefore they
contain mostly charged or polar residues, are frequently involved in its interactions or in
ligand binding (see section 4.3), and are commonly the sites of phosphorylation,
glycosylation and other protein modifications.