Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
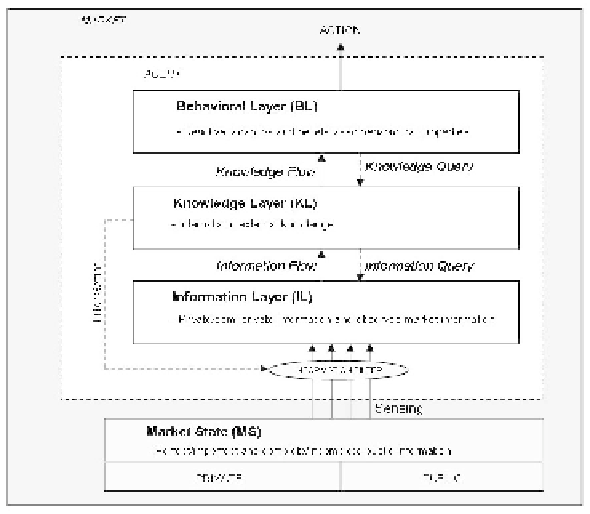
Fig. 1.
Structure of the IKB Model
3.1
The Information Layer
This section deals with how an agent gathers information which is then passed on to the
KL. The KL will select the data being stored in the IL by modifying the information
filter (see figure 1) appropriately. This filter will screen the data from the MS with some
noise (due to environmental noise or the agent's sensory limitations). As a result, the IL
of an agent will contain a noisy, restricted view of all information which it can observe.
Furthermore, the IL will also contain information about the agent's state,
p
i
(
t
),aswell
as its action set
A
i
.
We distinguish between information and knowledge in the following way:
Definition 4.
Information.
Information is raw data that can be sensed by an agent.
Definition 5.
Knowledge.
Knowledge is the processed data that is computed by an
agent from the information it has gathered.
Now, information is typically categorised as follows [15]:
-
Complete/Incomplete: An agent has complete information if it is aware of the com-
plete structure of the market (that is, its action sets and the result of each action).
Otherwise, it has incomplete information.
-
Perfect/Imperfect: An agent has perfect information if it is certain of its state, the
history of the market's and the agent's states (
H
(
p
M
(
t
k−
1
)) and
H
(
p
i
(
t
k−
1
)))that
have led it into this state. Otherwise, it has imperfect information.